| |
|
|
Updated July 2016
|
What are the latest developments regarding sexual policy matters?
With a landmark Supreme Court ruling in June 2015, the gay marriage controversy has been put to a rest. In Obergefell v. Hodges, the court ruled that state-level bans on same-sex marriage are unconstitutional. The rapid national and global acceptance of same sex marriage has been a remarkable development which has occurred entirely in the 21st century.
Why talk about sexuality and public policy? Isn't sexual behavior purely a personal matter?
While there are obvious civil liberty issues concerning social and governmental oversight of personal sexual behavior, human sexuality is in fact an activity which is highly regulated by society through custom, religion and legislation. Even those who adopt a libertarian attitude toward sexuality tend to respect modern social prohibitions regarding certain behaviors, e.g. incest, rape, and sex involving children. By contrast, historically some these practices have been tolerated to varying degrees in certain cultures while many other practices currently considered acceptable have been prohibited. In general, prevailing sexual behaviors are consistent with and governed by prevailing social attitudes.
The most clear relationship between sexuality and public policy is the institution of marriage. Marriage has existed in most societies as a religious and civil institution which encourages an association in which sexuality can be privately and exclusively expressed by each partner. Marriage and the offspring from this sexual union form a family unit which receives virtually universal social and governmental recognition as the primary building block of a civil society. Parents are provided with broad governmental powers within the family unit. Society's inheritance and benefit rules are uniformly tied to marriage and family.
Hasn't the "sexual revolution" changed everything?
Yes and no. Sexual behaviors have changed, particularly in many industrialized countries. It is fair to conclude that this is a dynamic situation and that civil and religious institutions are still adjusting to these changes. In addition, serious research has shed some light on a topic which had not been previously subjected to academic analysis.
Some generalizations emerge from this research:
- There are distinct differences between the sex drives of men and women.
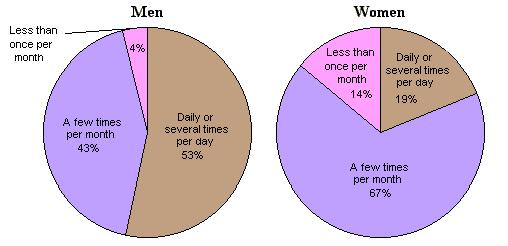
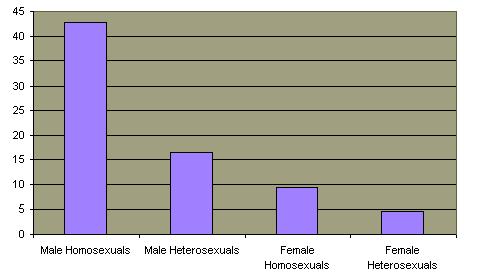
In modern society women have achieved tremendous economic and political gains. This has unquestionably included a greater freedom for individual sexual expression. But even a casual analysis of everyday life reveals significant differences in sexual appetite. With rare exceptions, women do not purchase pornography, patronize prostitutes or become sex offenders. Studies show that men have many more sexual fantasies  (Click to see chart) and lifetime sexual partners. (Click to see chart) and lifetime sexual partners.  This is not to suggest that men are by nature promiscuous and women are asexual. Throughout history most men and women have experienced a shared "romantic love" which combines sexuality with intense feelings of tenderness and monogamous attachment. This is not to suggest that men are by nature promiscuous and women are asexual. Throughout history most men and women have experienced a shared "romantic love" which combines sexuality with intense feelings of tenderness and monogamous attachment.
Sexual behavior is strongly influenced by habit.
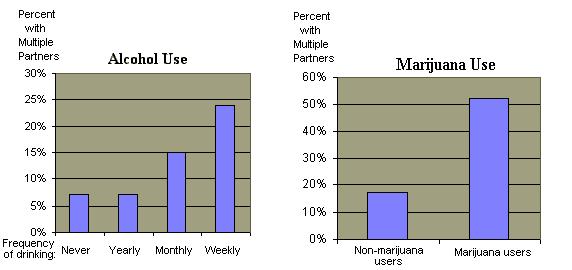
Sexual experiences produce a euphoria which is quite similar to the pleasure experienced by users of recreational drugs. Indeed there is a significant relationship between drug and alcohol use and the multiplicity of sexual partners.  (Click to see chart) In recent years "twelve step" "sexual addiction" programs modeled after drug/alcohol treatment programs have emerged for persons who are dissatisfied with their compulsive sexual behaviors. As the experiences of Senator Gary Hart and President Bill Clinton illustrate, the strength of such compulsions can be powerful and destructive to family life and career. For many individuals sexual habits can be modified. For example, in prisons some heterosexual inmates temporarily adopt homosexual behaviors and then revert to heterosexuality when released. (Click to see chart) In recent years "twelve step" "sexual addiction" programs modeled after drug/alcohol treatment programs have emerged for persons who are dissatisfied with their compulsive sexual behaviors. As the experiences of Senator Gary Hart and President Bill Clinton illustrate, the strength of such compulsions can be powerful and destructive to family life and career. For many individuals sexual habits can be modified. For example, in prisons some heterosexual inmates temporarily adopt homosexual behaviors and then revert to heterosexuality when released. - Society's "sexual norm" is a monogamous relationship between a man and woman.
Even with the decline in the marriage rate and the increased tolerance of homosexuality, the overwhelming majority of individuals still confine sexual behavior to a single, exclusive partner. This pattern has existed throughout human history and can be viewed as a compromise between male and female sexual needs. Males benefit from this arrangement because they are spared the task of constantly seeking new partners and confronting the many conflicts which would occur in an "open market". But the arrangement does deprive men of the sexual variety many of them might otherwise prefer. Women have traditionally benefited from this arrangement by obtaining someone who will provide security for the family unit even if it means accommodating the male's somewhat greater sex drive.
Because of the strong social investment in monogamy and the institution of marriage, it is not surprising that deviations from this standard meet with varying degrees of social opposition. This tension is at the root of the public policy controversy surrounding alternative sexual behaviors and "family values". Does increased tolerance of alternative behaviors increase their practice? Should society even endorse some of these behaviors?
- There is an increased social focus on sexuality in modern society.
In modern free market economies, sexual imagery is very commonly used as an advertising and promotional tool. It is reflected in modern clothing fashions. Sexual themes frequently are the subject of modern television programs and movies and the subject is often dealt with explicitly. Sexuality is now examined seriously by academics and mental health practitioners. The result of these developments is that sexuality is no longer an "underground" topic but has instead achieved a very visible and prominent place in modern consciousness. For example, many individuals who engage in homosexual or bisexual behaviors now define themselves in terms of a "sexual identity" and this concept governs their sense of self and of their role in society to a greater extent than other individual traits or personality characteristics. It is safe to conclude that in modern society many decisions, including the selection of a marriage partner, are guided more by a need for personal sexual satisfaction rather than by custom or social mores.
Sexuality Links
Google Directory - Politics of Sexuality
The Social Dimension of Sex Explores sexual issues from a social perspective.
The Alan Guttmacher Institute A non-profit organization focused on sexual and reproductive health research, policy analysis and public education.
Kinsey Institute
The Electronic Journal of Human Sexuality
Foundation for the Advancement of Sexual Equity
Wikipedia-Sex Positive Movement
|
Charts
(click to enlarge)
Rate of Sexual Fantasies for Men and Women
Average Lifetime Number of Sexual Partners
Relationship of Alcohol and Marijuana Use to Multiple Sex Partners in Past Year
|
|
MARRIAGE
What is the present status of marriage?
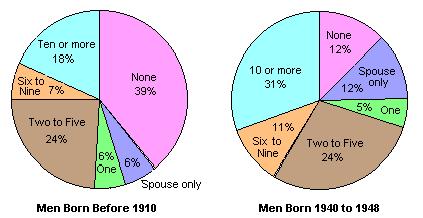
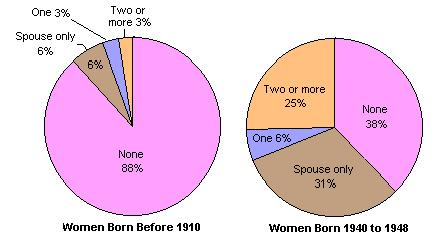
There has been a significant revolution in sexual behavior which began with the "baby boomer" generation born in the 1940s. Both men  and women and women  born in that generation were far more likely to have engaged in premarital sex when compared to previous generations. A substantial percentage of high school seniors now believe that cohabitation before marriage is a desirable option. born in that generation were far more likely to have engaged in premarital sex when compared to previous generations. A substantial percentage of high school seniors now believe that cohabitation before marriage is a desirable option.  Many couples are now cohabitating instead of marrying and an increasing percentage of unmarried couples have families with children. Many couples are now cohabitating instead of marrying and an increasing percentage of unmarried couples have families with children.  In fact, almost a majority of unmarried mothers are cohabitating with the child's father. In fact, almost a majority of unmarried mothers are cohabitating with the child's father.  The majority of unmarried mothers are no longer teenagers. The majority of unmarried mothers are no longer teenagers. 
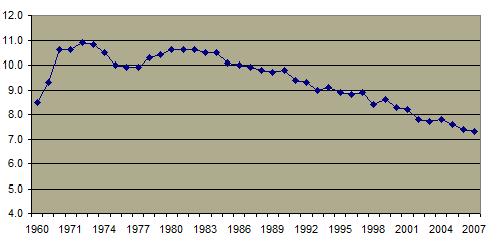
One result has been an overall decline in the marriage rate. Census data indicates that the marriage rate has steadily decreased  and the percentage of adults who are married has also significantly decreased. and the percentage of adults who are married has also significantly decreased.  . There has also been a substantial decline in the percentage of persons who report their marriages to be satisfying. . There has also been a substantial decline in the percentage of persons who report their marriages to be satisfying.  The divorce rate skyrocketed between 1960 and 1980 and has remained at a high level since then. The divorce rate skyrocketed between 1960 and 1980 and has remained at a high level since then.  A substantial percentage of individuals have been married more than once. A substantial percentage of individuals have been married more than once.  The birth rate has also decreased The birth rate has also decreased  although not in the same proportion. Thus there are far more single parent families. although not in the same proportion. Thus there are far more single parent families.  The percentage of births to unmarried women has climbed steadily and dramatically especially since 1960. The percentage of births to unmarried women has climbed steadily and dramatically especially since 1960. 
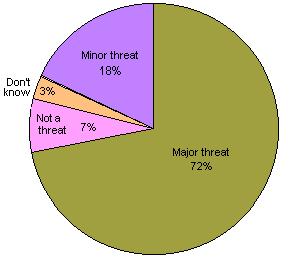
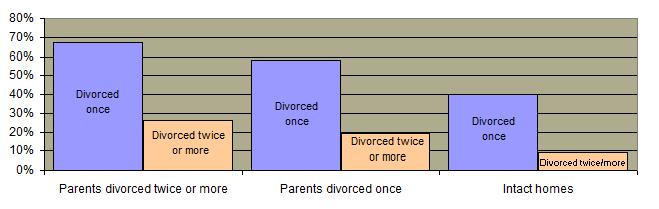
These trends have generated significant public concern. Although the majority of Americans believe that divorce is acceptable in some situations  , they believe that it is a major threat to family values. , they believe that it is a major threat to family values.  Children of divorced parents are also more likely to divorce themselves. Children of divorced parents are also more likely to divorce themselves. 
What has caused this phenomenal increase in divorces?
There are several interrelated factors:
- Improved economic status of women
In modern societies, women are capable of achieving independent economic status. As a result, they can choose to leave marriages which are unsatisfactory. This has affected men as well because they do not suffer from extreme social ostracism if they abandon their wives and families.
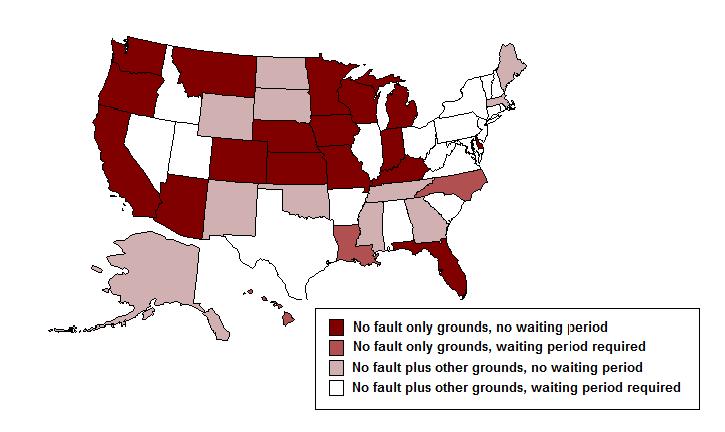
- The development of "no fault" divorce
In 1969, California became the first state to modify divorce laws to permit either spouse to obtain a divorce based upon irreconcilable differences. All states now have some sort of "no fault" divorce; in several it is the only basis for divorce.  This change in law was a response to the expense and demands that an increasing divorce rate had placed on the nation's judicial systems. But the removal of legal obstacles has also substantially contributed to the acceleration of the divorce rate. This change in law was a response to the expense and demands that an increasing divorce rate had placed on the nation's judicial systems. But the removal of legal obstacles has also substantially contributed to the acceleration of the divorce rate.
- Changing marital expectations
The marital vow "till death do us part" has become more of a mutual hope than an absolute promise. Frequently when either marriage partner realizes that their initial expectations are not being met, they divorce. Sometimes the decision is mutual; other times it is unilateral. It is fair to observe that most often the divorce decision is primarily based on the spouse's perceived personal welfare and that the effect of the decision on children and on the overall social system receives much less consideration.
What is the situation in other countries?
There is indeed an international aspect to these trends. The U.S., Cuba, Russia and other former Soviet bloc countries have the world's highest divorce rates. 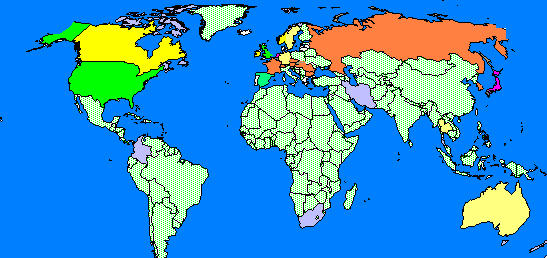 The marriage rate in many European countries has declined substantially and the rate of births to unmarried women has risen dramatically in European countries. The marriage rate in many European countries has declined substantially and the rate of births to unmarried women has risen dramatically in European countries.  However, a greater percentage of European unmarried mothers are cohabitating with the fathers of their children. In most countries, the percentage of single parent families is increasing, but the U.S. rate is significantly higher. However, a greater percentage of European unmarried mothers are cohabitating with the fathers of their children. In most countries, the percentage of single parent families is increasing, but the U.S. rate is significantly higher. 
What reforms are being proposed?
The decrease in marriage and the high divorce rate has generated concern, particularly with religious leaders, and now a slight majority of Americans believe it should be harder for individuals to obtain a divorce.  Arizona and Louisiana have enacted legislation which permit optional "covenant marriages" which allow divorce only for cause or by mutual consent. Proposals for a more comprehensive return to a "fault-based" divorce system have not yet obtained sufficient legislative support. It is unclear whether social and religious concern about "family values" will increase and whether society will experience a reversal of current demographic trends. Arizona and Louisiana have enacted legislation which permit optional "covenant marriages" which allow divorce only for cause or by mutual consent. Proposals for a more comprehensive return to a "fault-based" divorce system have not yet obtained sufficient legislative support. It is unclear whether social and religious concern about "family values" will increase and whether society will experience a reversal of current demographic trends.
Marriage Links
Google Directory - Marriage
WIkipedia - Marriage
Wikipedia - Divorce in the United States
Alliance for Marriage
Americans for Divorce Reform
Family Research Council
Focus on the Family
Traditional Values Coalition
|
Charts
(click to enlarge)
Number of Pre-Marital Sexual Partners for Males
Number of Pre-Marital Sex Partners for Women
Percentage of High Schools Seniors Prefering Cohabitation Before Marriage
Unmarried Coupled Households 1960-2005
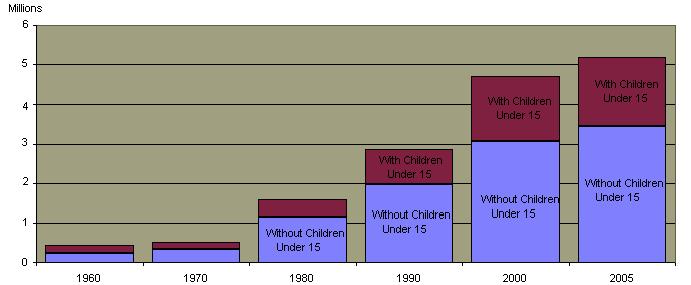
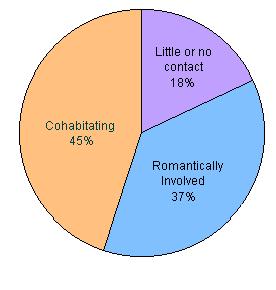
Relationship of Unmarried Mother to Child's Father
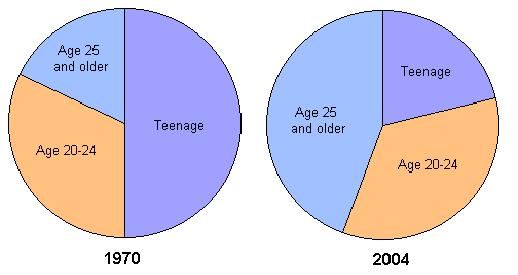
Percentage of Non Marital Births by Age of Mother
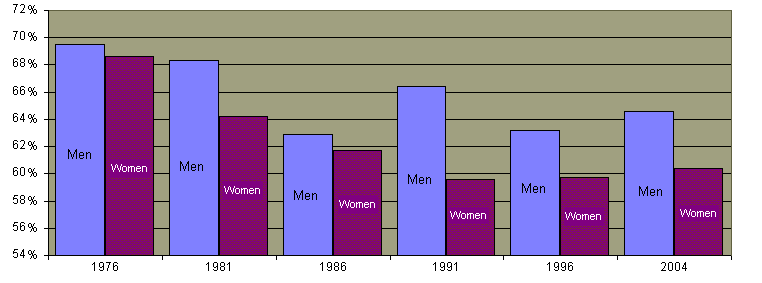
Percentage of Married Persons Age 35 through 44
Percentage of Persons Aged 15 or Over Who Are Married
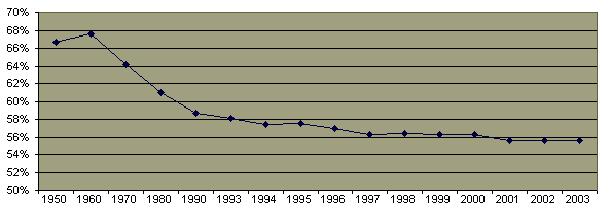
Percentage of Men and Women Reporting "Happy Marriages"
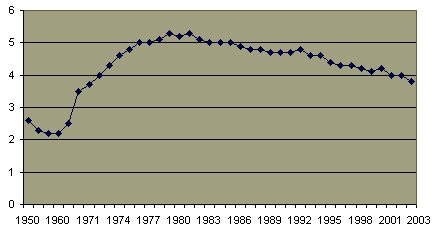
Divorce Rate Per 1000 Persons, 1950-2003
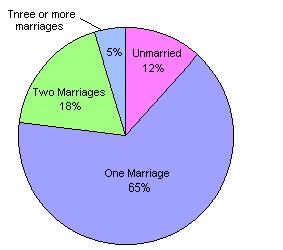
Frequency of Marriage, Adults 25-74
Status of Adults Aged 40-59
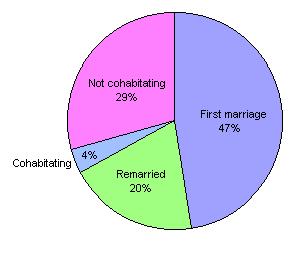
Birth Rate Per 1000 1950-2003
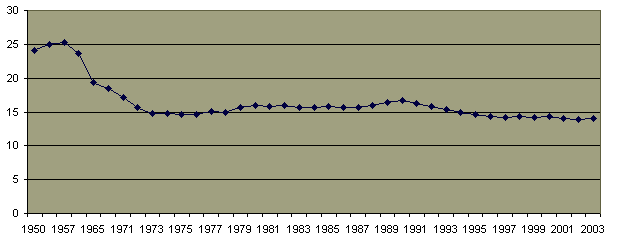
Percentage of Children Not Lving With Both Parents 1980-2004
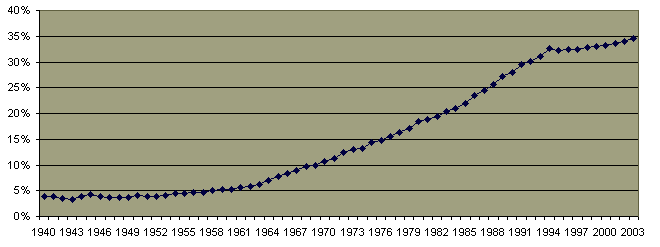
Percentage of Births to Unmarried Mothers 1940-2003
Public Opinion on Divorce
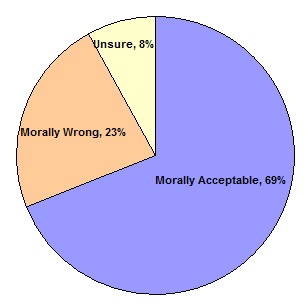
Public Opinion on Divorce Effect on Family Values
Divorce Rate Based On Parent's Divorced History
State No Fault Divorce Legislation
Divorces Per 1000 Persons By Country
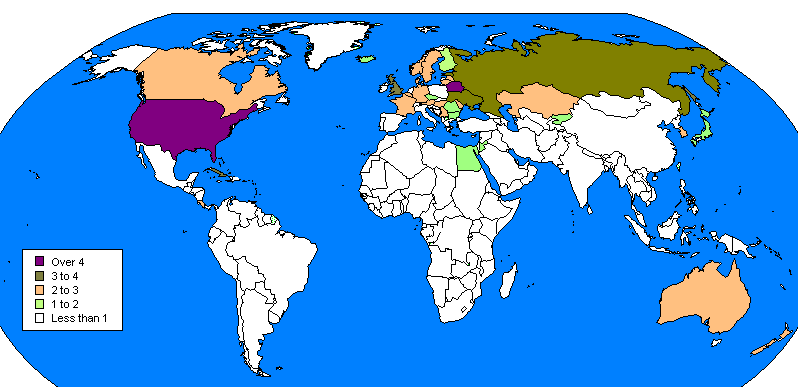
Percentage of Births to Unmarried Mothers in Selected European Countries
Comparison of Single Parent Households in Selected Countries
|
|
HOMOSEXUALITY
Has there been a change in social attitudes regarding homosexuality?
Definitely.
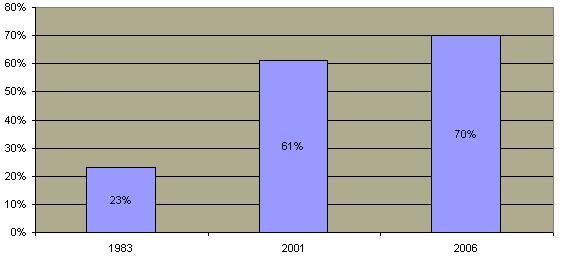
Although homosexuality has existed throughout history, its practice has been socially discouraged in most societies by custom, religion and law. Until the 1970's, homosexual acts between consenting adults were criminal in most states. Most states repealed such "sodomy" laws in the past three decades  and the laws were seldom enforced in the states that did not repeal them. In 2003, the Supreme Court ruled all such laws to be unconstitutional. In 1973, the American Psychiatric Association removed homosexuality from its list of mental and emotional disorders. A majority of Americans now consider homosexuality an acceptable alternative lifestyle. and the laws were seldom enforced in the states that did not repeal them. In 2003, the Supreme Court ruled all such laws to be unconstitutional. In 1973, the American Psychiatric Association removed homosexuality from its list of mental and emotional disorders. A majority of Americans now consider homosexuality an acceptable alternative lifestyle.  In the past decade, the number of Americans opposed to gay persons adopting children has decreased although the trend appears to be changing. In the past decade, the number of Americans opposed to gay persons adopting children has decreased although the trend appears to be changing. 
The modern trend toward greater social acceptance of homosexuality continues. Same sex marriage is now legal throughout the United States and in a growing number of countries.  In a major victory for supporters of gay rights, the military policy of dismissing openly gay soldiers was rendered illegal by Congress in December 2010. In a major victory for supporters of gay rights, the military policy of dismissing openly gay soldiers was rendered illegal by Congress in December 2010.  (Click to see chart) This legislative landmark was preceded by the 2009 addition of sexual orientation to hate crimes legislation. (Click to see chart) This legislative landmark was preceded by the 2009 addition of sexual orientation to hate crimes legislation.
Nonetheless there remains a significant social stigma associated with the practice of homosexuality in mainstream society. Among male heterosexuals, homosexuality is rarely discussed and almost never in positive terms. Despite such a strong social stigma, at least a quarter of adult men who are or have been married have engaged in homosexual behavior.  Homosexuals, most particularly male homosexuals, are subject to routine ridicule and employment discrimination. Many experts believe that this social aversion, labeled "homophobia" by the gay community, is related to subconscious repression of homosexual desires by heterosexuals. Homosexuals, most particularly male homosexuals, are subject to routine ridicule and employment discrimination. Many experts believe that this social aversion, labeled "homophobia" by the gay community, is related to subconscious repression of homosexual desires by heterosexuals.
Is homosexuality determined at birth? How widespread is its practice?
The factors which influence the choice of homosexuality are poorly understood. Many homosexuals claim to have had these desires from their earliest memories and some current research has suggested that there may be subtle brain differences between homosexual and heterosexuals. Most experts believe that sexual orientation is shaped for most people at an early age through complex interactions of biological, psychological and social factors.
The reality is that "homosexuality" is probably too variable a concept to be analyzed in this fashion. It is clear that some men, particularly those whose interests and attitudes can be categorized as "feminine", may have no capacity whatsoever to develop a sexual attraction for the opposite sex. This also applies to some homosexual women, particularly those whose interests and attitudes can be classified as "masculine". But many homosexuals, probably a majority of practicing homosexuals, cannot be categorized in this fashion. These individuals, often influenced by random life events and personal associations, have developed a desire to practice sexuality in this fashion in preference to other options available to them. A thorough research study conducted among homosexuals in the San Francisco area in 1973 supports this conclusion. A clear majority of the homosexual men studied had experienced heterosexual relations and a significant number had experienced heterosexual dreams.  The acknowledgement of heterosexual dreams and fantasies by members of this group is significant because most were quite committed to their adopted homosexual lifestyle. The acknowledgement of heterosexual dreams and fantasies by members of this group is significant because most were quite committed to their adopted homosexual lifestyle.
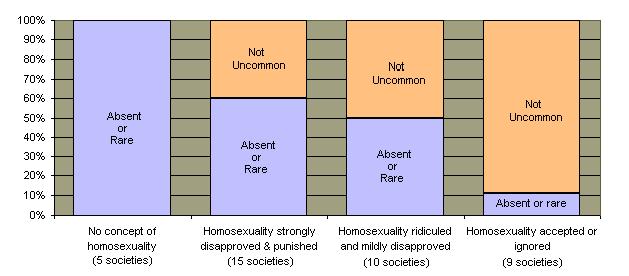
If homosexuality is primarily regarded as a preference governed at least in part by personal choice, then its variable prevalence in societies can be more easily understood. Anthropological studies indicate that the prevalence of homosexuality is directly related to the prevailing social attitude toward the practice.  The incidence of homosexuality in the United States has always been difficult to determine because many "closeted" homosexuals keep their status secret. Many others disclose their status only to a small circle of friends. But it is unquestionable that the recent trend toward tolerance of homosexuality has vastly increased the number of persons who choose to adopt this lifestyle. Many more Americans now have homosexual friends or acquaintances. The incidence of homosexuality in the United States has always been difficult to determine because many "closeted" homosexuals keep their status secret. Many others disclose their status only to a small circle of friends. But it is unquestionable that the recent trend toward tolerance of homosexuality has vastly increased the number of persons who choose to adopt this lifestyle. Many more Americans now have homosexual friends or acquaintances.  Homosexual "enclaves" have emerged in many large cities. In such areas it has become far easier for homosexuals to associate without risking social disapproval and harassment. Homosexual "enclaves" have emerged in many large cities. In such areas it has become far easier for homosexuals to associate without risking social disapproval and harassment.
Are committed homosexual couples comparable to heterosexual married couples?
The few studies that are available suggest that there are differences in sexual behavior. However it is unlikely that there are any significant differences in the level of emotional commitment.
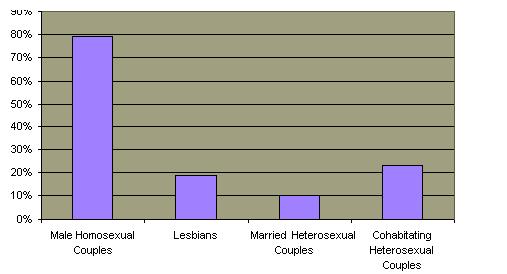
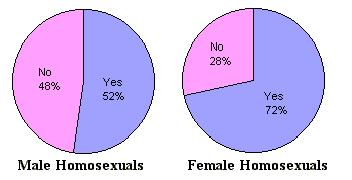
Male homosexuals, even when coupled, are unlikely to confine their sexual behavior to their partner.  In contrast to female homosexuals and heterosexuals, the majority of male homosexual encounters are between strangers In contrast to female homosexuals and heterosexuals, the majority of male homosexual encounters are between strangers  even though a slight majority of such homosexuals are also involved in a sexual affair. even though a slight majority of such homosexuals are also involved in a sexual affair.  This accounts for the extraordinarily high lifetime numbers of partners that male homosexuals have. This accounts for the extraordinarily high lifetime numbers of partners that male homosexuals have. 
Although female homosexual couples are far more likely to be faithful to each other, studies indicate that female homosexuals have sex with much less frequency than heterosexual couples and that an absence of sexual desire becomes a common complaint in many of these long term relationships.
The sexual behavior of married couples is quite different. It is quite apparent that the institution of heterosexual marriage is a powerful vehicle for promoting regular and monogamous sexual behavior. This pattern of behavior does not appear to be significantly affected by the degree of sexual activity the partners may have had prior to the marriage. Still, studies indicate that there is infidelity in approximately a quarter of heterosexual marriages.
It can be debated as to whether the degree of sexual fidelity is relevant to a discussion of the gay marriage issue as there is little doubt that the levels of emotional commitment are very similar between gay unions and heterosexual unions. In some cultures where prostitution is widely tolerated, there are higher levels of heterosexual male infidelity than in the U.S..
How has the AIDs epidemic affected male homosexual behavior?
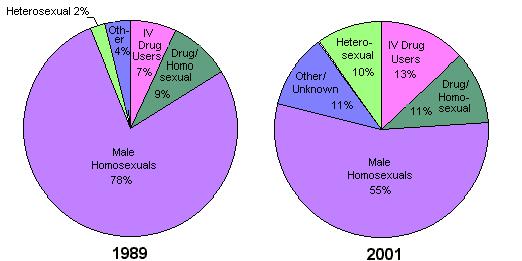
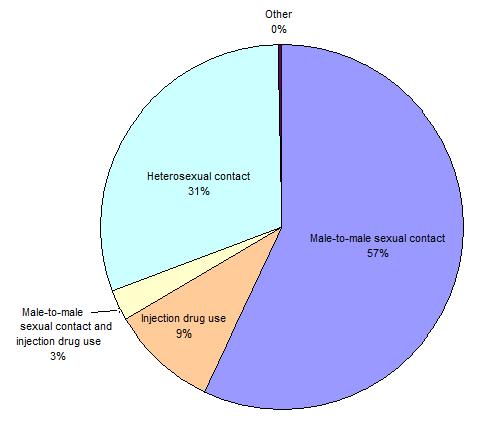
A major difficulty with the promiscuity associated with male homosexuality has been the high rate of venereal disease. The emergence of the AIDs virus in the early 1980's marked the arrival of a sexually transmitted disease that was fatal. The response of the gay community to this threat was impressive. There is no doubt that "safer sex" practices combined with the fear of AIDS had a profound and salutary effect on the health of homosexual men in general. The incidence of new cases of HIV, hepatitis B virus, gonorrhea, and syphilis, all other sexually-transmitted diseases, and AIDS decreased dramatically in the gay community. This was due to an increased use of condoms, more care in choosing partners, decreased promiscuity, and a decrease in the sex practices that were particularly high risk. The result is that the homosexual share of California AIDS cases has dropped substantially in the past decade.  Even so, the CDC estimates that in 2009 the majority of new HIV infections in the United States were through homosexual transmission. Even so, the CDC estimates that in 2009 the majority of new HIV infections in the United States were through homosexual transmission. 
What political issues have emerged regarding homosexuals?
- Discrimination
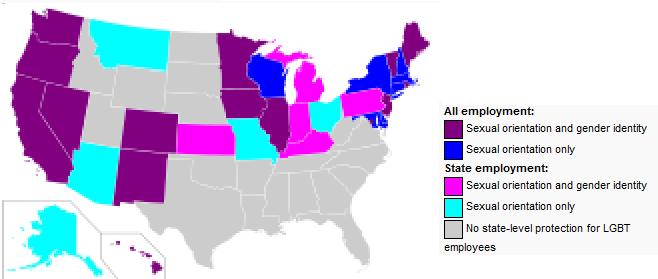
Despite its increased public acceptance, most states still do not have laws which protect gay people from discrimination in employment, housing and health care.  The lack of consensus on this issue is reflected by the numbers of Senators and Representatives who have not adopted non-discrimination policies for the hiring of the office staffs. The lack of consensus on this issue is reflected by the numbers of Senators and Representatives who have not adopted non-discrimination policies for the hiring of the office staffs. 
A particularly difficult aspect of the discrimination problem has involved the Boy Scouts of America. Although the Boy Scouts is a private organization, its activities are part of the fabric of mainstream America. The organization has long maintained a policy of excluding Scout participants and leaders who have been discovered to be homosexual. In June 2000, the United States Supreme Court, in a 5-4 vote invalidated a New Jersey court ban on the dismissal of a homosexual scout leader based on the New Jersey anti-discrimination law. Because part of the Boy Scout's mission is to provide young men with role models, its discrimination policy blends the "tolerance v. legitimacy" dialectic which has characterized the gay rights debate. The difficulty of this issue is reflected in a recent Senate vote regarding whether public schools should be allowed to ban the Boy Scouts from facilities based on their anti-gay policies. 
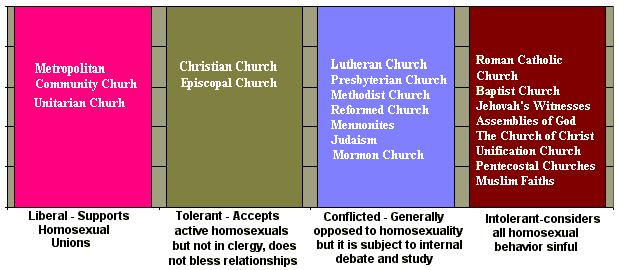
The Boy Scout policy is in part based on religious principles (the organization also bans atheists and agnostics). The status and level of inclusion of gays and lesbians in organized religion is a question of debate in many major denominations and religious groups.  The traditional view of most religions is that sexuality is to be confined to a monogamous heterosexual marriage. The growing social acceptance of homosexuality strongly challenges that view especially when it is considered that monogamy is quite rare in committed male homosexual relationships. The traditional view of most religions is that sexuality is to be confined to a monogamous heterosexual marriage. The growing social acceptance of homosexuality strongly challenges that view especially when it is considered that monogamy is quite rare in committed male homosexual relationships.
- Military service
A major aspect of the discrimination issue involves the military. In December 2010, the long standing military policy of discharging homosexuals was invalidated by legislation action.
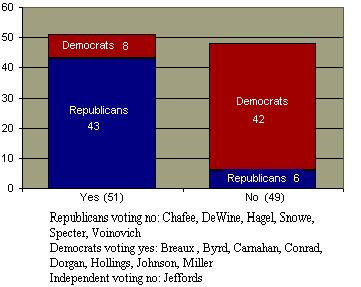
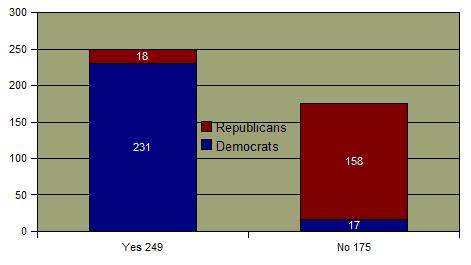
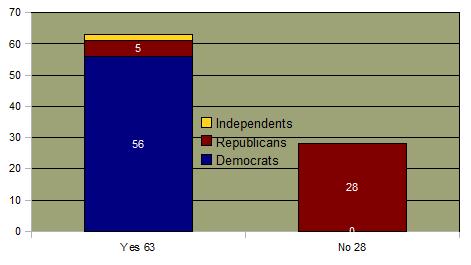
See Senate Vote See House Vote Although the policy has been repealed, it is not likely to be implemented until 2012. The prior military policy required the exclusion of individuals who have been discovered to have engaged in homosexual behavior. These rules had been upheld by the U.S. Supreme Court. In the aftermath of the election of President Clinton in 1991, there was a reexamination of this policy. Military leadership and conservative political forces strongly resisted elimination of the exclusionary policy and it was decisively defeated in the Senate at that time.  Ultimately, Congress passed legislation forbidding the military from aggressively investigating suspected homosexual behavior, the so-called "don't ask, don't tell" policy. Ultimately, Congress passed legislation forbidding the military from aggressively investigating suspected homosexual behavior, the so-called "don't ask, don't tell" policy.  Subsequent to the enactment of the policy, there was little effect on the rate of military discharges except during few years just prior to the recent legislation.. Subsequent to the enactment of the policy, there was little effect on the rate of military discharges except during few years just prior to the recent legislation..  At the time of the legislative reversal of the policy, public opinion overwhelmingly supported the rights of gays to serve openly in the military. At the time of the legislative reversal of the policy, public opinion overwhelmingly supported the rights of gays to serve openly in the military. 
- Hate crime legislation
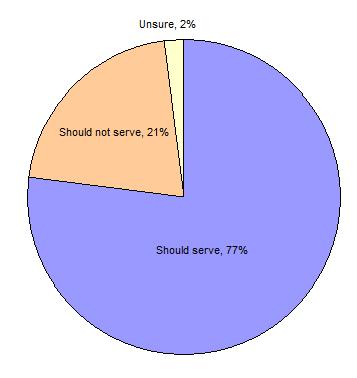
Perhaps due to the greater political visibility of homosexuals, there has been an increase in hate crimes related to sexual orientation.  Federal hate crime legislation to include sexual orientation was finally passed by the House Federal hate crime legislation to include sexual orientation was finally passed by the House  and Senate and Senate  in 2009 and was signed by the President in October 2009. Prior to the enactment of this legislation, a slim majority of states had included sexual orientation in hate crime legislation. in 2009 and was signed by the President in October 2009. Prior to the enactment of this legislation, a slim majority of states had included sexual orientation in hate crime legislation. 
Homosexuality Links
Google Directory - Same Sex Marriage
Yahoo Directory - Gay Marriage
Google Directory - Boy Scouts Controversy
Google Directory, Gay Military Service
Yahoo Directory - Gays in Military
Google Directory, Hate Crimes
Yahoo Directory - Hate Crimes
Google Directory, Homophobia
Google Directory, Sexual Orientation
Wikipedia - Same Sex Marriage
Wikipedia - Boy Scout Controversy
Wikipedia - Gays in Military
Wikipedia - Hate Crimes
Wikipedia - Homophobia
Wikipedia - Sexual Orientation
Gay rights:
ACLU: Gay and Lesbian Rights
Queer by Choice - radical gathering place for those who have chosen to be gay, and rejects studies that reflect a genetic source for homosexuality.
Anti-gay rights:
National Association for Research and Therapy of Homosexulality
|
Charts
(click to enlarge)
States with Sodomy Laws in 2003
Percentage of Amercians Who Consider Homosexuality to be Acceptable Lifestyle
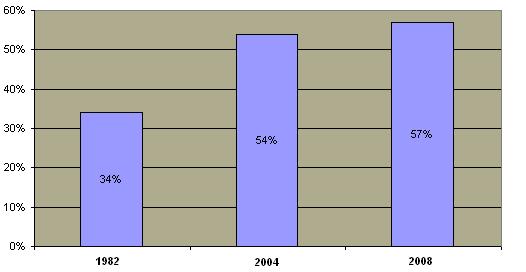
Percentage of Public Opposed to Gay Adoption
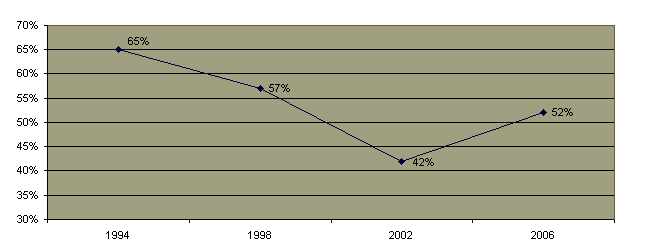
Reported Homosexual Contact by Currently or Previously Married Men
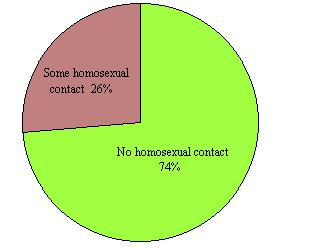
Heterosexual Experiences of Surveyed Homosexual Males
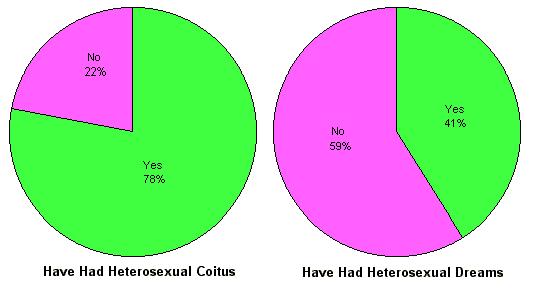
Prevalence of Homosexuality in Selected Societies
Persons Reporting Having Gay Friend or Acquaintance
Percentage of Couples Where at Least One Partner was not Monogamous in Past
Year
Percentage of Sexual Partners Who Were Strangers
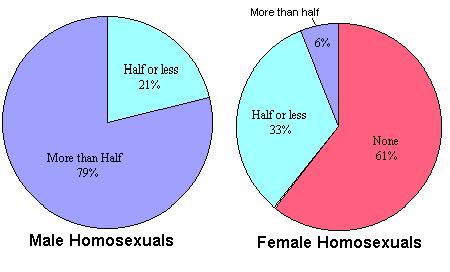
Percentage of Homosexuals Involved in Current Affair
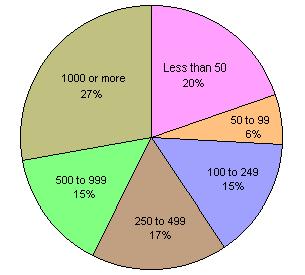
Lifetime Number of Partners of Survey San Francisco Area Male Homosexuals
AIDS Cases By Exposure Category in California
Estimated Sources of New HIV Infection 2009
State Laws on Workplace Discrimination Based on Sexual Orientation
Senators and Representatives Adopting Sexual Orientation Non Discrimination Policy for Office Staff
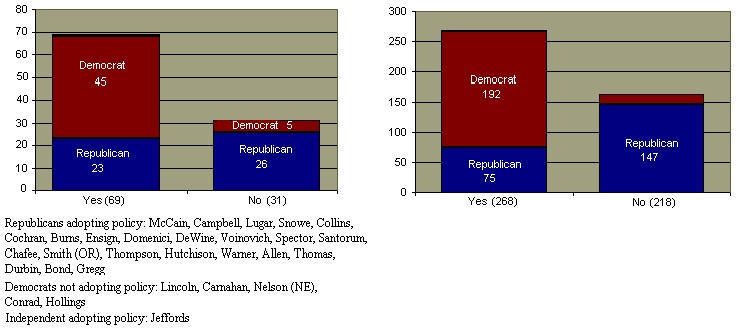
Senate Vote on Measure to Ban Federal Funding To Schools Who Prohibit Boy Scout Use of Facilities
Attitudes of Organized Religions on Homosexuality
Final Vote Repealing Don't Ask Don't Tell
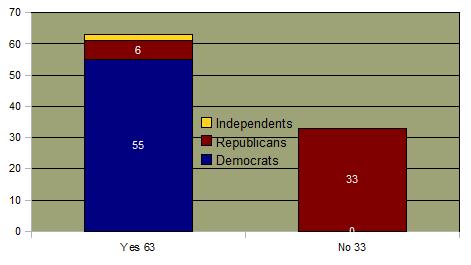
Repealing Don't Ask Don't Tell
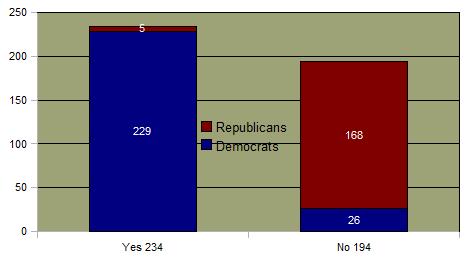
Senate Vote on Permitting Homosexuals in the Military
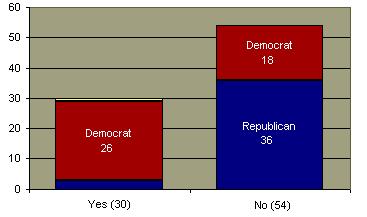
House Vote on Don't Ask Don't Tell
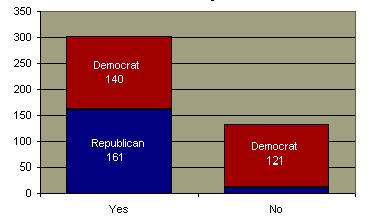
Military Discharges Based on Homosexuality 1980-200
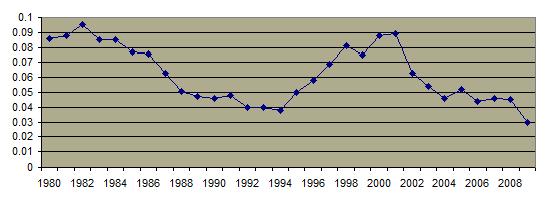
Public Opinion on Gays Serving Openly in the Military
Statistics on Hate Crimes Involving Homosexuals

Expansion of Hate Crimes Legislation
Including Sexual Orientation in Hate Crimes Legislation
State Legislation on Sexual Orientation and Hate Crimes
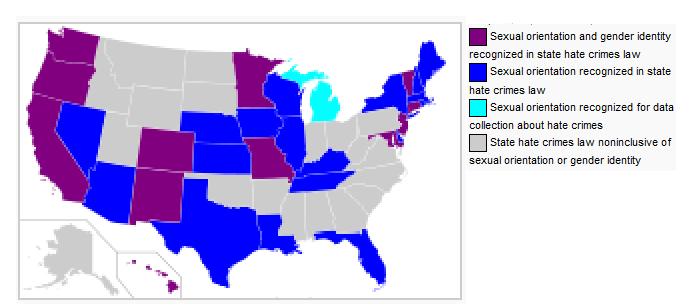
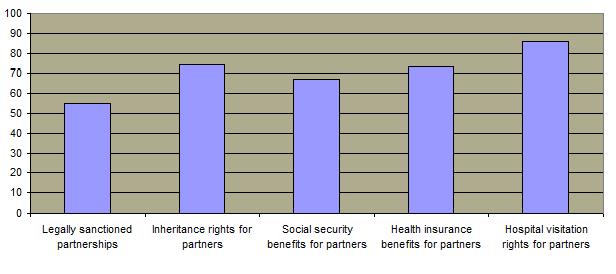
Status of Gay Relationships in U.S.

Public Opinion on Domestic Partnerships
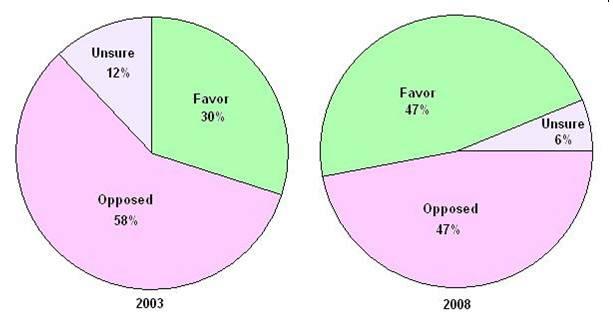
Public Opinion on Gay Marriage
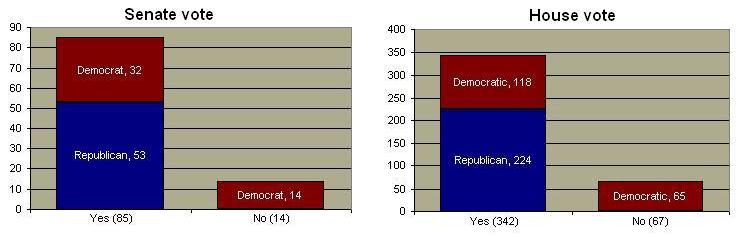
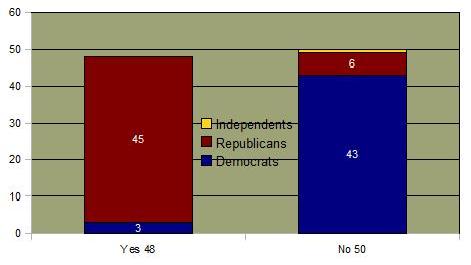
Congressional Vote on Defense of Marriage Act
Constitutional Amendment Limiting Marriage to Heterosexuals
|
|
PROSTITUTION
How prevalent is prostitution in the United States?
It is very difficult to measure the prevalence of prostitution in the United States, but it is much lower than in Europe and than in many less developed countries.
This was not always true. Prostitution holds a major, if underreported, position in the annals of American history. During the years of massive immigration into this country, there was a frequent shortage of women. Although prostitution was always illegal, brothels and free-lance prostitutes were a common aspect of urban life even at the beginning of the 20th century
What changed? Prostitution was a victim of the same moral wave that prompted the Volstead Act and brought the country into the era of prohibition. These changes were accomplished by an enforcement zeal at the local level. Once the institutional structure of prostitution was dismantled, it has occupied a relatively low degree of visibility since. Even with the relaxation of sexual mores, there has been no major resurgence, perhaps in part because many men today have other options for premarital or extramarital sex. Prostitution is legal today in a few rural areas of Nevada and tolerated in very few other communities. Sexual survey data supports the diminished influence of prostitution in American sexual life during the past century. 
Today prostitution is conducted by streetwalkers who congregate in run-down urban areas and at truck stops (the lowest rungs of the prostitution hierarchy), massage parlor workers (the next highest rung), bar and hotel girls (a little higher up than the massage parlor workers), and call girls and escort service workers (the highest rungs). In addition to traditional prostitution, many cities have "adult entertainment" establishments where women physically interact with customers. There are also "phone sex" services where women discuss sexual fantasies with customers. Men also perform similar services for homosexual customers. There appear to be no reliable studies which estimate the total number of such "sex workers" and the percentages of individuals in each type of occupation.
Why do men seek prostitutes?
Despite its relatively low profile and the fact that police vice operations often vigorously control its practice, prostitution does exist and there are customers who are willing to risk exposure and prosecution by patronizing them. In countries where there is more tolerance of prostitution, the demand for services is quite high.
Studies have shown that the customers of prostitutes fit no particular profile psychologically or socially. The only common characteristic is that most appear to have a high sex drive. A slight majority of the men who pay for prostitutes are married or cohabitating and the vast majority have been married or have cohabitated at one time. 
The demand for prostitution can best be understood in the overall context of male sexuality. As with homosexuality, most men appear to have the ability to enjoy the experience of sexuality with a minimal need for intimacy. These men may have and enjoy intimate relationships with women but such relationships do not fully satisfy their sexual desires. It is probable that many married men refrain from using prostitutes not because the idea is repugnant but because it would be an act of disloyalty to their marriage partner or otherwise against their moral values.
Is prostitution a "victimless" crime?
In many countries, the demand for such services outweighs the supply of women who choose to provide them. As a result, there is widespread importation of women from economically disadvantaged countries. Quite often such women are lured into the work through misrepresentation by racketeers or even through sale by parents. Many are children. Such individuals are quite clearly victims.
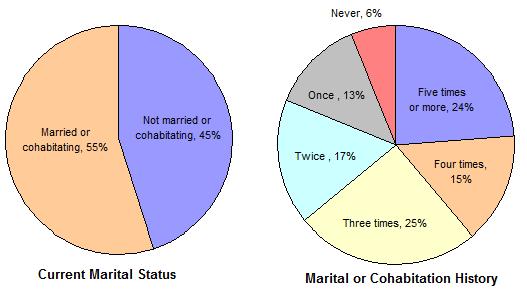
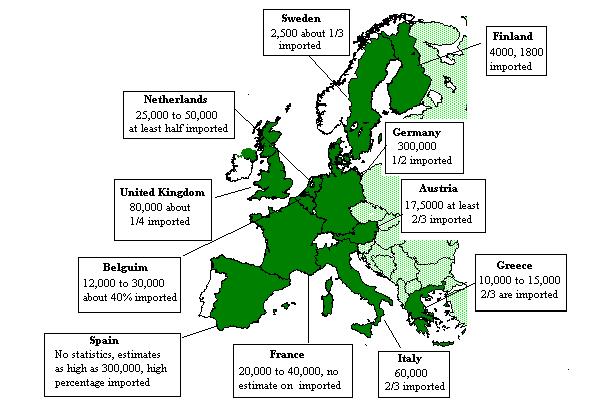
This trafficking does occur in the United States. According to the CIA, an estimated 45,000 to 50,000 women and children are trafficked annually to the United States and a majority of such women are forced into prostitution.  In addition, the American military regularly facilitates the use of prostitutes by overseas American servicemen in third world countries. In addition, the American military regularly facilitates the use of prostitutes by overseas American servicemen in third world countries.
In the United States, a large percentage of "street" prostitutes come from very disadvantaged backgrounds. Many use prostitution to support a drug habit for themselves and for a male companion. These prostitutes experience high rates of sexual violence even while not working. Many were involuntarily introduced into prostitution as adolescents by manipulative pimps.
"Non-street" prostitutes come from more stable backgrounds. But a majority of these prostitutes were sexually abused as children, most often through incest, although the estimates of the exact percentage vary widely. The suicide rate of prostitutes is quite high according to some studies.
But not all prostitutes consider themselves victimized. Some prostitutes, calling themselves "sex workers", have formed organizations which are supportive of this lifestyle. They note that is an unskilled job that has high financial rewards. Many such organized prostitutes profess to enjoy their work and endeavor to reduce the social stigma and criminality which is attached to it.
The feminist community is somewhat divided on the prostitution issue. The predominant view is that prostitution is a servile vestige of a male dominated society. But other feminists take the position that prostitution is acceptable as long as the prostitute has control of her circumstances and exercises free choice to use her body to satisfy male sexual appetites. They thus support the "prostitute's rights" movement.
The reality is that prostitution has very low appeal as an occupation for most women. It confers very low social status on the women involved, thus estranging them from normal social associations. This is why the pay is comparatively high and why there is trafficking in such women as if they were a commodity.
Are prostitutes contributing to the spread of the AIDS epidemic?
Prostitution has a large role in the global spread of the epidemic but a relatively minor role in the United States. Studies indicate that the incidence of HIV among U.S. prostitutes who have not used intravenous drugs is quite low; less than one percent. The overall rate of female to male transmission in the United States is also very low so there is very minimal transmission of the virus from prostitutes to customers even when condoms are not used. It is the prostitutes themselves who have a higher risk of contracting HIV from customers or male lovers when they have unprotected sex. Although exact estimates are not available, it is believed that all but a very small percentage of prostitutes in the U.S always use condoms with customers. In the legal brothels in Nevada, the use of condoms is mandatory and universal.
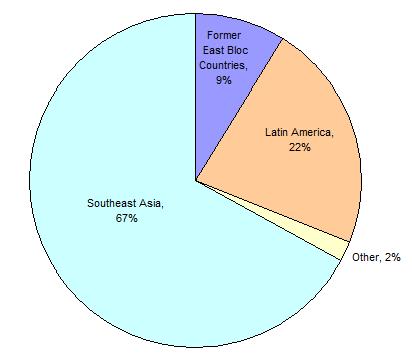
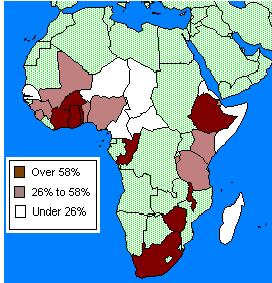
In Sub-Saharan Africa  prostitution has been a major cause of the devastating epidemic. Prostitution continues to be major factor in causing new cases Southeast Asia, particularly Thailand, Myanmar and Cambodia. prostitution has been a major cause of the devastating epidemic. Prostitution continues to be major factor in causing new cases Southeast Asia, particularly Thailand, Myanmar and Cambodia.  The common denominator in the spread of AIDs in both Thailand and Africa has been a cultural acceptance of the promiscuity associated with prostitution. The common denominator in the spread of AIDs in both Thailand and Africa has been a cultural acceptance of the promiscuity associated with prostitution.  Because of malnutrition and a high rate of other untreated sexually transmitted diseases, particularly in Africa, the disease has been more contagious and the rate of transmission from female to male and male to female is about the same. Thailand has promoted a 100% condom use policy for prostitutes Because of malnutrition and a high rate of other untreated sexually transmitted diseases, particularly in Africa, the disease has been more contagious and the rate of transmission from female to male and male to female is about the same. Thailand has promoted a 100% condom use policy for prostitutes  and has achieved significant success in its reducing its rate of new HIV infections and has achieved significant success in its reducing its rate of new HIV infections  and of venereal disease in general. and of venereal disease in general.  The percentage of prostitutes who are HIV positive has also decreased significantly. The percentage of prostitutes who are HIV positive has also decreased significantly. 
What is the international status of prostitution?
Prostitution is tolerated to a far greater extent in Europe  and in less developed countries although very few countries completely legalize the practice. According to the International Labor Organization, the commercial sex industry in Southeast Asia has grown into a key economic sector. In Thailand it accounts for 14 percent of the GDP and as many women are employed as sex workers as are employed in manufacturing. The economic transition of the countries in the former Soviet bloc has displaced many women from their sources of income and forced them into prostitution. and in less developed countries although very few countries completely legalize the practice. According to the International Labor Organization, the commercial sex industry in Southeast Asia has grown into a key economic sector. In Thailand it accounts for 14 percent of the GDP and as many women are employed as sex workers as are employed in manufacturing. The economic transition of the countries in the former Soviet bloc has displaced many women from their sources of income and forced them into prostitution.
The apparent constant in prostitution is the demand for such services when they are available. Quite obviously, in areas where the practice is tolerated, millions of men use prostitutes every day and expend substantial amounts of money in the process. By contrast, in less tolerant societies, the demand for the service is much less.
The problem of prostitution trafficking in general, and particularly the trafficking in children has attracted the attention and concern of many throughout the world. The international community began meeting in 1999 to draft a Protocol to Prevent, Suppress, and Punish Trafficking in Persons, especially Women and Children in conjunction with the U.N. Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime. The U.N. General Assembly adopted the Convention and the Protocol on Trafficking in November 2000. The United States has passed legislation which requires the State Department to report to Congress regarding efforts world countries are making to punish traffickers and deter this trade. The 2001 report lists 23 countries which have failed to make sufficient efforts. 
Prostitution Links
Google Directory - Sex Work
Google Directory - Anti-Trafficking
Wikipedia - Prostitution
Wikipedia - Prostitution by Country
Wikipedia - Sex Tourism
Prostitute's Education Network (information service about legislative and cultural issues as they effect prostitutes and other sex workers)
Prostitution Research and Education Website (an anti-prostitution feminist site)
Factbook on Global Sexual Exploitation
Sex work and Sexual Exploitation in the European Union
|
Charts
(click to enlarge)
Status of American Males Who Use Prostitutes
Source of Women Trafficked to the United States
Percentage of Prostitutes Infected With HIV in Selected African Countries
Types of AIDs Transmission in Southeast Asia, 2007
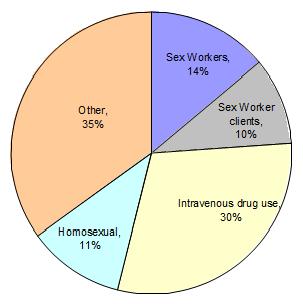
Thai and Kenyan Males Reporting Nonregular Sex Partners
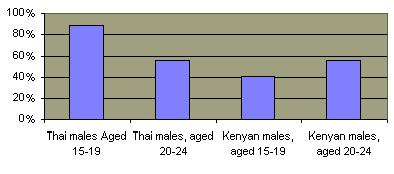
Condum Use Among Thai Prostitutes
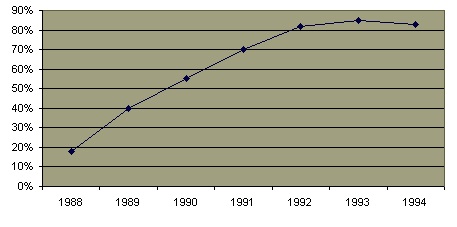
New HIV Infections Among Thai Military Conscripts
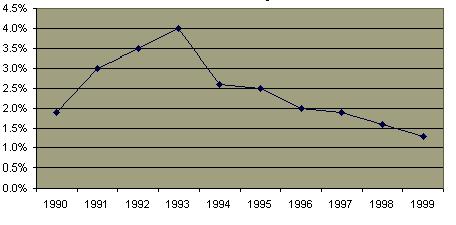
Decline in Sexually Transmitted Disease in Thailand
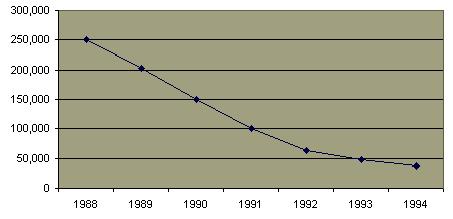
Prevalence of HIV Among Thai Brothel Prostitutes
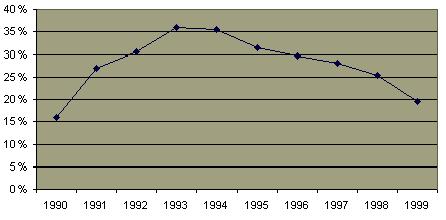
Estimate of Prostitution in Europe
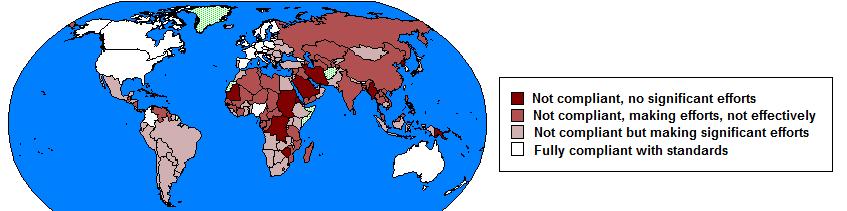
U.S. State Department Evaluation of Compliance with Trafficking Conventions, 2010
|
|
PORNOGRAPHY
What is the impact of pornography?
The graphic depiction of sexuality in various forms of media is relatively new in the United States. The change began in the late 60's primarily as a result of Supreme Court decisions which applied stringent First Amendment protections to much of this material.
The political reaction to this change resulted in the establishment of two Presidential commissions for the purpose of studying this subject.
The commission report issued during the Lyndon Johnson administration concluded that there was little evidence of a relationship between pornography and sexual criminal behavior and that in fact there was evidence that it might lead to a reduction in such behaviors. The commission's report recommended sex education, funding of research into the effects of pornography, restriction of children's access to pornography, and recommended against any restrictions for adults. The report was widely criticized and rejected by Congress.
In 1985, President Ronald Reagan appointed another commission to study pornography issues. It was headed by Attorney General Edwin Meese. The commission's report, released in 1986, found that pornography is harmful and can lead to violent acts. The scholarship of this report has been widely criticized.
As with prostitution, the feminist position on pornography is divided. Most believe that pornography contributes to the "objectification" of women and are strongly opposed to it. Others believe that participation in this business is acceptable if women are not exploited in the process.
There is overwhelming condemnation of child pornography primarily because of the exploitation of children necessary to produce these materials. Criminal laws strictly prohibit the sale and distribution of child pornography and offenders are vigorously prosecuted.
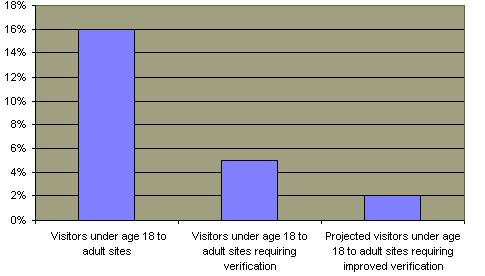
Today pornography is big business and the internet has developed into a major source of pornographic content.  Only 30% of Americans believe pornography to be morally acceptable although there is more acceptance of the practice among younger Americans. Only 30% of Americans believe pornography to be morally acceptable although there is more acceptance of the practice among younger Americans.  The primary public policy concern regarding pornography at present involves the internet. A substantial percentage of visitors to the adult sites on the Internet are children although this percentage could be substantially reduced by effective regulation. The primary public policy concern regarding pornography at present involves the internet. A substantial percentage of visitors to the adult sites on the Internet are children although this percentage could be substantially reduced by effective regulation.  Legislative efforts are underway to regulate minors' access to these materials in a manner which is constitutionally permissible. Legislative efforts are underway to regulate minors' access to these materials in a manner which is constitutionally permissible.
The overall impact of pornography is still a subject of debate. Contrary to what might be expected, studies have shown that there is a negative correlation between pornography and sexual criminal behavior. On the other hand, the proliferation and easy access to pornographic materials is unquestionably a major contributor to "sex addiction" behaviors. Such behaviors substantially interfere with the overall social functioning of many males in modern society.
Pornography Links
Google Directory - Pornography
Google Directory - Pornography and Sex Addiction
Yahoo Directory - Pornography
Wikipedia - Pornography
Wikipedia - Internet Pornography
Victims of Pornography
National Academy: Youth, Pornography, and the Internet
The effects of Pornography: An International Perspective
|
Charts
(click to enlarge)
Revenues of Pornography Industry, 2006
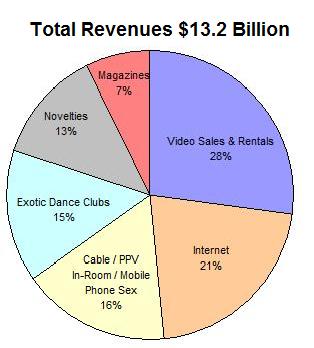
Americans Who Believe Pornography to be Morally Acceptable
Use of Internet Pornography By Minors
|
|
TEEN SEXUAL BEHAVIOR
Has teenage sexual behavior changed?
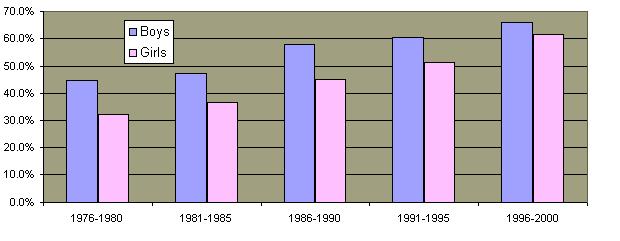
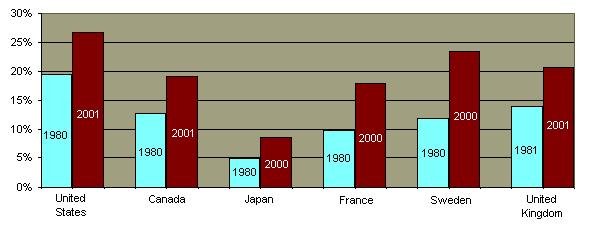
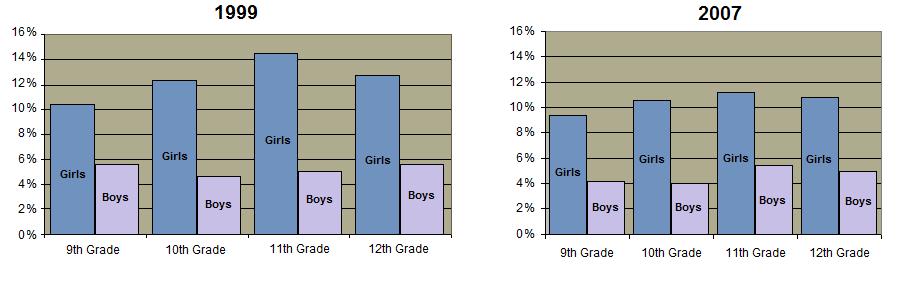
Since 1960 there has been a dramatic increase in teenage sexual activity although the trend is beginning to reverse.  The percentage of high school students who have had sex has diminished.
The percentage of high school students who have had sex has diminished.  Those who are sexually active tend to have fewer partners. Those who are sexually active tend to have fewer partners.  The association between sexual activity and drug use has diminished somewhat but it is still very significant. The association between sexual activity and drug use has diminished somewhat but it is still very significant. 
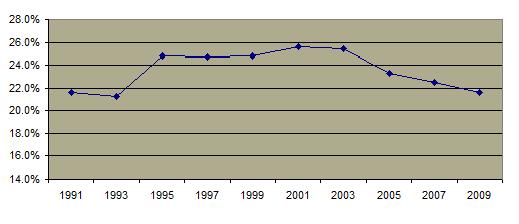
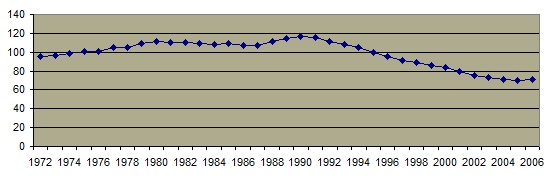
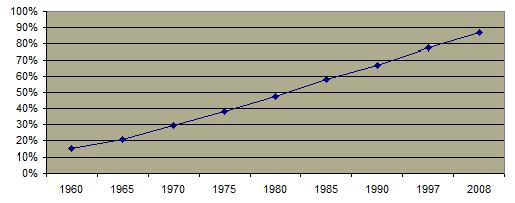
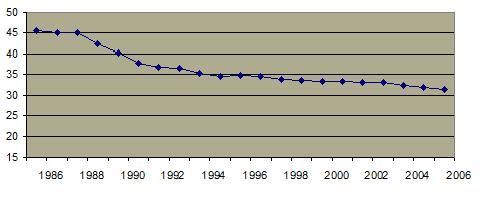
The teen pregnancy rate has significantly diminished.  The decrease in sexual activity is probably not as important to this trend as has been welfare reform (which eliminated an incentive for teen pregnancy among low income groups) and the increased availablity and use of contraception. The pregnancy rate is highest in the southern states The decrease in sexual activity is probably not as important to this trend as has been welfare reform (which eliminated an incentive for teen pregnancy among low income groups) and the increased availablity and use of contraception. The pregnancy rate is highest in the southern states  In 1999, over 10% of high school seniors have become pregnant or gotten someone pregnant. In 1999, over 10% of high school seniors have become pregnant or gotten someone pregnant.  The percentage of teenage mothers who are unmarried has increased from about 15% in 1960 to almost 90% in 2008. The percentage of teenage mothers who are unmarried has increased from about 15% in 1960 to almost 90% in 2008.  The percentage of teenage pregnancies which are terminated by abortion has declined since the 1980's. The percentage of teenage pregnancies which are terminated by abortion has declined since the 1980's. A significant percentage of teen girls and boys report having been forced to engage in sexual intercourse against their will although that number is also decreasing. A significant percentage of teen girls and boys report having been forced to engage in sexual intercourse against their will although that number is also decreasing. 
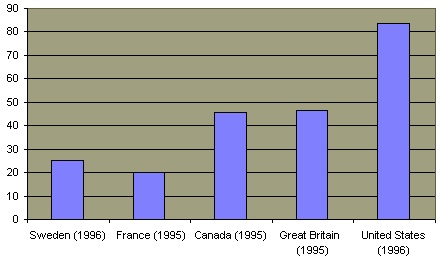
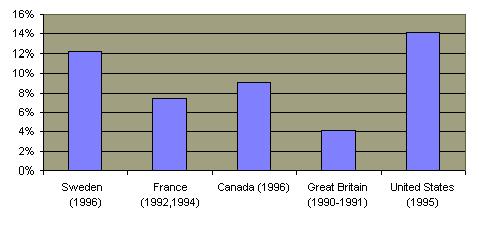
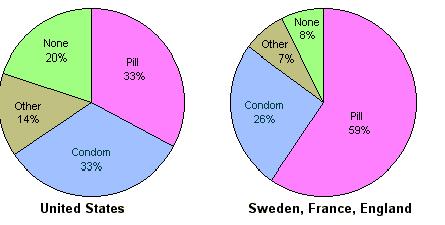
The teenage pregnancy rate is far lower in Europe and Canada than it is in the United States  due to less sexual activity due to less sexual activity  and greater use of contraception in those countries. and greater use of contraception in those countries. 
Teen Sexual Behavior Links
Google Directory - Teen Sexuality
Google Directory - Teen Pregnancy Prevention
Wikipedia - Adolescent Sexuality
Guttmacher Institute - Adolescents
CDC-Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System
Kaiser Family Foundation - Teen Sex Fact Sheet
|
Charts
(click to enlarge)
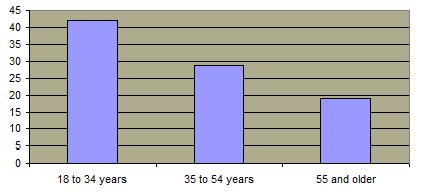
Percentage of American Teen Women Who Have Had Sex, By Age
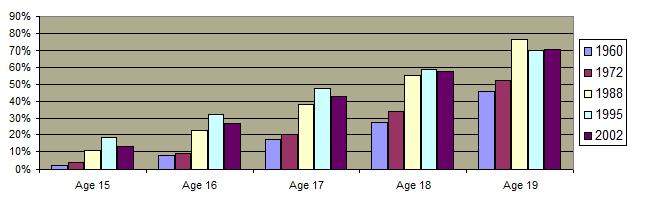
Percentage of High School Students Who Have Had Sex 1991-2009
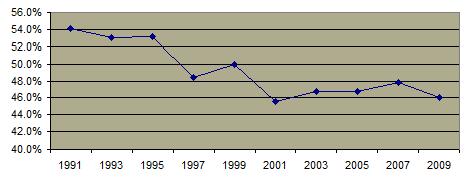
Percentage of High School Students Having Sex With Four or More Partners 1991-2009
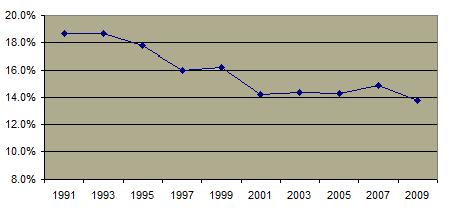
Percentage of Sexually Active High School Students Using Drugs or Alcohol at Time of Last Sexual Intercourse
Teenage Pregancy Rate Per 1000 Women Aged 15-19, 1972-2006
Pregnancy Rate Per 1000 Teen Women By State
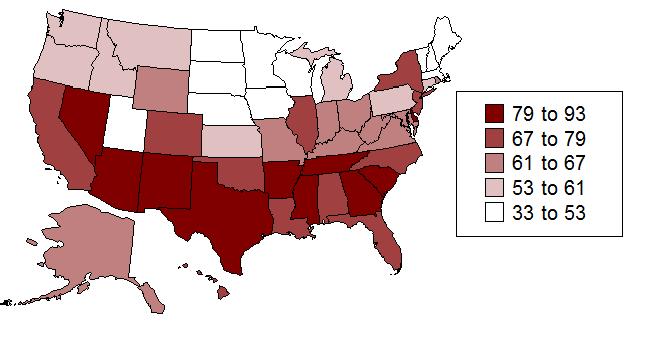
Percentage of High School Students Who Have Been Pregnant or Who
Percent of Unmarried Teenage Mothers 1960-2008
Percentage of Teen Births Resulting in Abortion 1986-2006
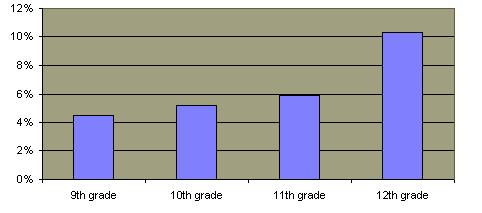
Percentages of High School Students Who Report Being Forced to Have Had Sex
Teen Pregnancies in Selected Countries Per 1000 Women
Percentage of Teenage Girls Having Sex Before Age 15 in Selected Countries
Comparative Contraception Use Between U.S. and European Teens
|
|
SEX EDUCATION
Sex education has become prevalent in recent decades. Has it improved teenage sexual behaviors?
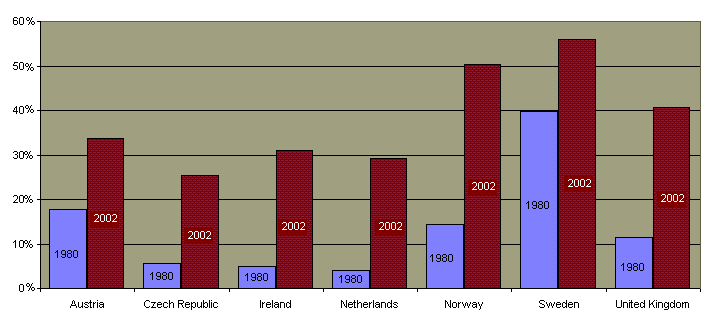
Sex education has indeed become more common in public schools. In the1970's only about 30% of high school students received such instruction. Many states now mandate that sex education and/or STD/HIV be covered in the public school curricula.  and a great majority of the country's secondary schools cover the subject. and a great majority of the country's secondary schools cover the subject. 
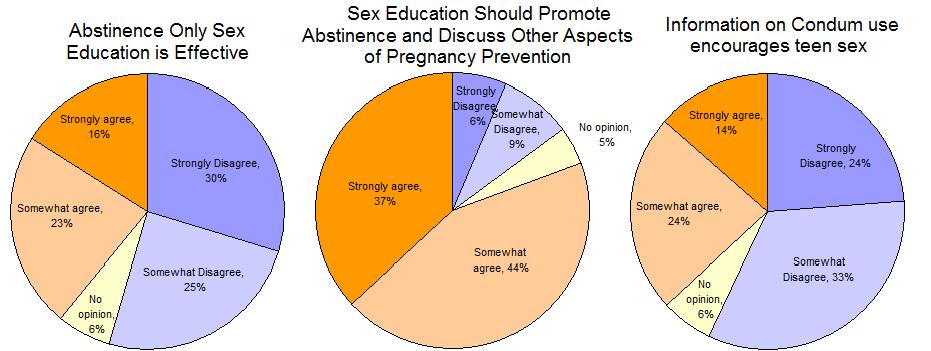
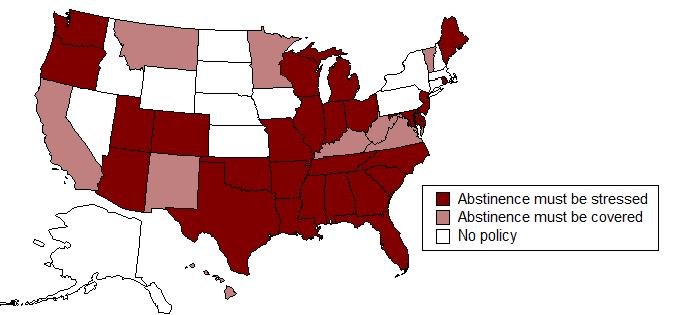
Public opinion is generally supportive of sex education and most Americans believe that more than just abstinence be discussed.  But the concept of sex education is not without controversy. Many religious groups are concerned that "comprehensive" sex education is supportive of the current prevalence of premarital sex. In response to this concern, over half of the states require that abstinence be covered or stressed in sex education courses.
Abstinence education has been spurred by Congressional action which provides funding for programs which stress abstinence. But the concept of sex education is not without controversy. Many religious groups are concerned that "comprehensive" sex education is supportive of the current prevalence of premarital sex. In response to this concern, over half of the states require that abstinence be covered or stressed in sex education courses.
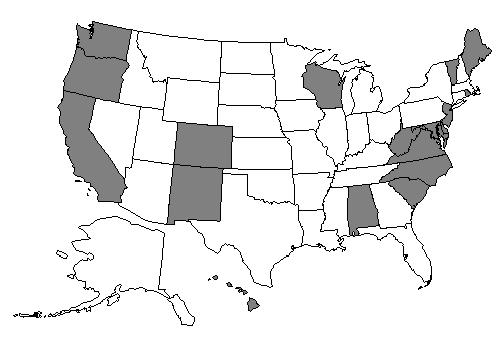
Abstinence education has been spurred by Congressional action which provides funding for programs which stress abstinence.  Seventeen states require local school districts that do offer sex education to cover information about contraception. Seventeen states require local school districts that do offer sex education to cover information about contraception. 
The effect of sex education on behavior appears to be significant if the program is comprehensive. For example a significant percentage of sexually active teenagers do use condoms  and condom use has significantly increased among high school students during the past decade. and condom use has significantly increased among high school students during the past decade. 
Sex Education Links
Google Directory - Sex Education
Google Directory - Sex Education - Abstinence
Wikipedia - Sex Education in the United States
Wikipedia - Abstinence Only Sex Education
Advocates For Youth - Sex Education
Sexuality Information and Education Council of the United States
|
Charts
(click to enlarge)
State Legislation on Sex Education

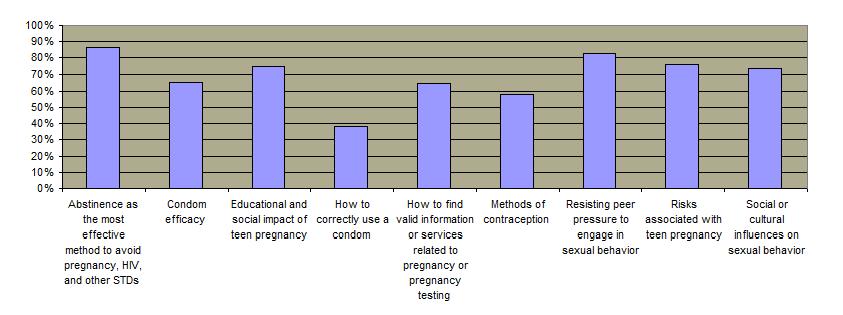
Percentage of Schools Offering Sex Education on Various Topics
Public Opinion on Type of Sex Education
State Policies on Abstinence as Part of Sex Education
States Requiring Sex Education to Include Contraception
Condum Use By Sexually Active High School Students, 2009
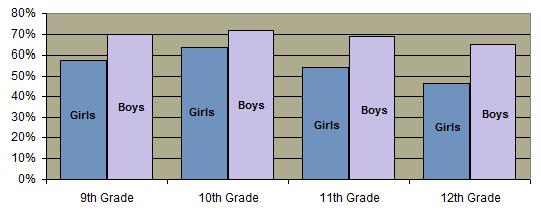
Percentage of Sexually Active High School Students Using Condoms
|
|
SEX IN THE MEDIA
What is the contribution of the media to the modern "revolution" in sexual behaviors?
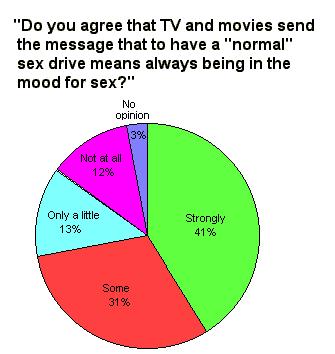
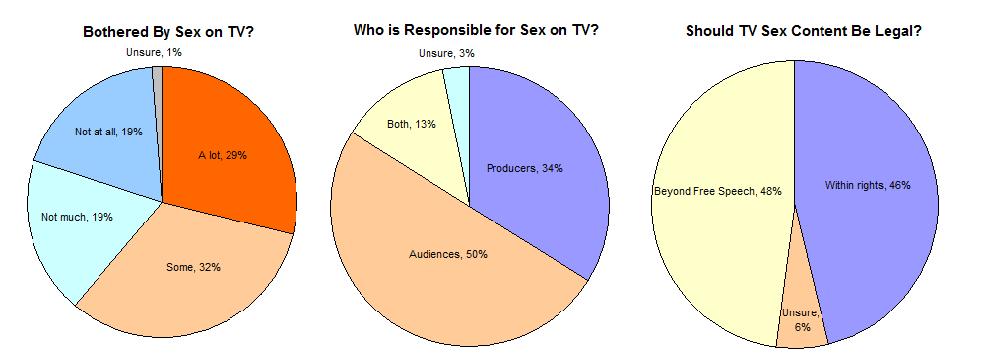
Sexuality is a very common topic in television programming although there is some evidence that this content is beginning to diminish.  Even though most adults do not believe that television portrays sex realistically Even though most adults do not believe that television portrays sex realistically  , there is evidence that these portrayals strongly influence attitudes and desires. Most adults, for example, believe that movies and television portray a normal sex drive as "always being ready for sex". , there is evidence that these portrayals strongly influence attitudes and desires. Most adults, for example, believe that movies and television portray a normal sex drive as "always being ready for sex".  American attitudes on this issue are ambivalent. A majority are concerned with the danger of government censorship but also believe that standards for sex and violence should be more stringent. American attitudes on this issue are ambivalent. A majority are concerned with the danger of government censorship but also believe that standards for sex and violence should be more stringent. 
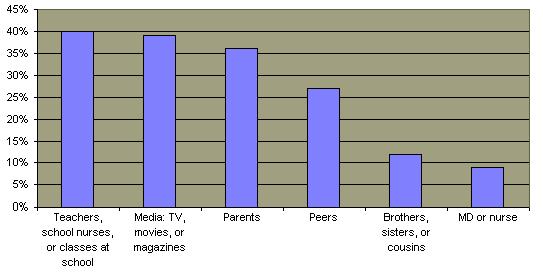
There is evidence that sexual content in the media particularly influence teenagers. Studies show that teenagers spend the almost the equivalent of a full work week receiving information from various forms of media and that the media is in fact a major source of sexual information for them. 
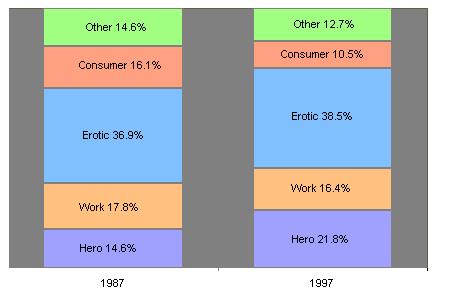
The major impact of the media on sexual attitudes may have less to do with programming than with the ubiquity of sexual content in advertising messages. The advertising industry quickly learned that one of the most powerful selling tools in a consumerist society is sex. Not only are women sexually objectified by advertising, but men are as well. Such images are now quite frequent in advertising materials designed for a male audience.  Some social observers have concluded that the prevalence of the sexual content in advertising has put sex on a pedestal and has caused Americans to place an unreasonable priority on sexual satisfaction. In the process, such personal self-satisfaction has become paramount to the commitment required to channel sexual activity into a lasting marriage. Even many non-religious Americans are beginning to conclude that the "sexual revolution" - the acceleration of the divorce rate, the prevalence of homosexuality, the massive sale of pornographic materials, the prevalence of teen sexual behavior - are byproducts of the use of sex by the advertising industry to sell products. Some social observers have concluded that the prevalence of the sexual content in advertising has put sex on a pedestal and has caused Americans to place an unreasonable priority on sexual satisfaction. In the process, such personal self-satisfaction has become paramount to the commitment required to channel sexual activity into a lasting marriage. Even many non-religious Americans are beginning to conclude that the "sexual revolution" - the acceleration of the divorce rate, the prevalence of homosexuality, the massive sale of pornographic materials, the prevalence of teen sexual behavior - are byproducts of the use of sex by the advertising industry to sell products.
Sex in the Media Links
Parents Television Council
Wikipedia - Sex in Advertising
Rand Corporation - Impact of Television Sex on Teen Behavior
|
Charts
(click to enlarge)
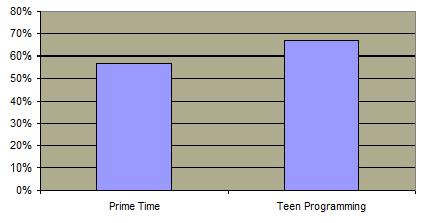
Percentage of Surveyed TV Entertainment Programming Where Sex is a Topic
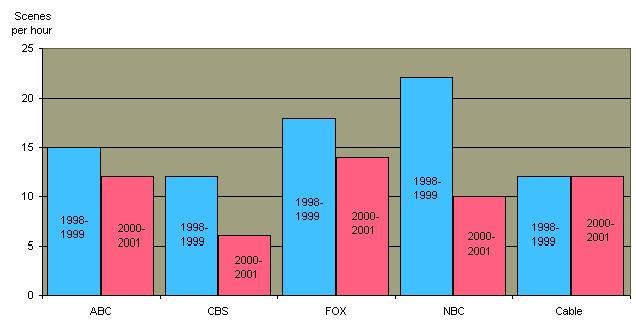
Amount of Sexual Material Per Hour
Public Opinion on How Realistic Sex is Portrayed on Television

Why Public Regards TV Portrayal of Sex as Unrealistic
Public Opinion About Sex on Television
Sources of Sex Information for Teens
Images of Men in Magazine Advertising 1987 and 1997
|
|
CRIMINAL SEXUAL BEHAVIOR
How prevalent is rape and other sexual crimes?
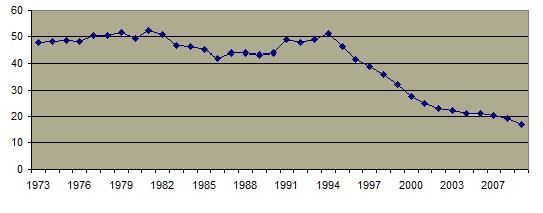
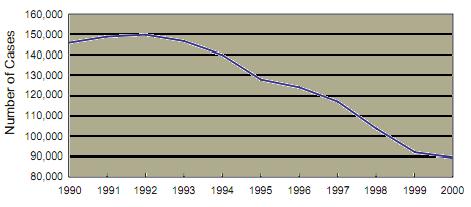
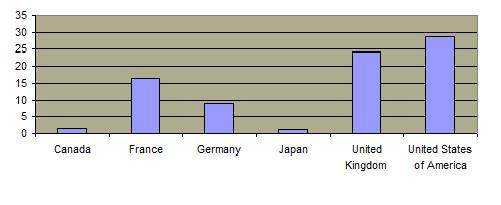
The incidence of rape in the United States has significantly decreased recently  at approximately the same rate most other crimes. at approximately the same rate most other crimes.  Similarly, the number of substantiated cases of child sexual abuse has declined. Similarly, the number of substantiated cases of child sexual abuse has declined.  But the rate of sexually related criminal behavior is much greater in the United States than it is in most other developed countries. But the rate of sexually related criminal behavior is much greater in the United States than it is in most other developed countries.  Almost one out of every 5 women has been a rape victim and over half the victims were 17 years old or younger at the time of the first rape. Almost one out of every 5 women has been a rape victim and over half the victims were 17 years old or younger at the time of the first rape. 
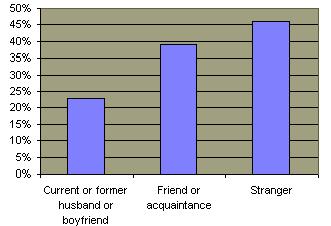
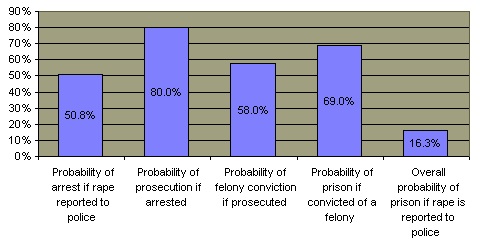
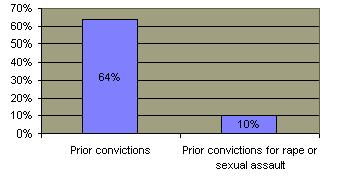
A substantial amount of rapes are not reported.  The closer the relationship between the female victim and the offender, the greater the likelihood that the police would not be told about the rape or sexual assault. The closer the relationship between the female victim and the offender, the greater the likelihood that the police would not be told about the rape or sexual assault.  Nevertheless, a majority of convicted rapists do have an acquaintance with their victim. Nevertheless, a majority of convicted rapists do have an acquaintance with their victim.  Of rapes that are reported, about half result in an arrest but less than 20% of such perpetrators actually serve a prison sentence. Of rapes that are reported, about half result in an arrest but less than 20% of such perpetrators actually serve a prison sentence. 
There is disagreement among researchers regarding whether rape is primarily a sexual crime or whether, as many women's advocates suggest, it is a crime which reflects male attitudes of dominance. The fact that the decrease in rape has been consistent with an overall decrease in violent crime actually suggests that sex may be the dominant motivation of most rapists. The rapist desires sex and is willing to "steal" sex by disregarding any consent by his partner. For this reason, many rapists also have extensive criminal records.  Like many criminals, their behavior is often associated with drug use. Like many criminals, their behavior is often associated with drug use.  Whether the rape is perpetrated by a career criminal or a "date rape" acquaintance, the common denominator is that the male has achieved sexual satisfaction without receiving the consent of the victim. Whether the rape is perpetrated by a career criminal or a "date rape" acquaintance, the common denominator is that the male has achieved sexual satisfaction without receiving the consent of the victim.
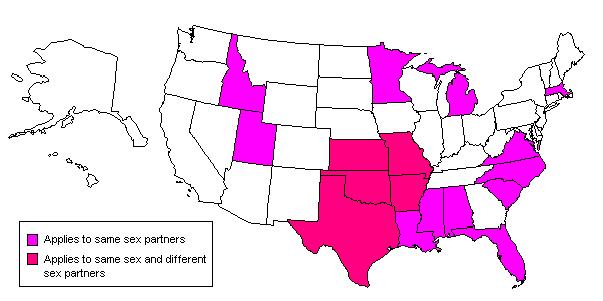
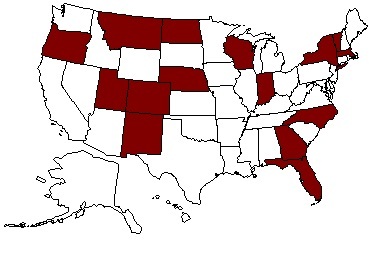
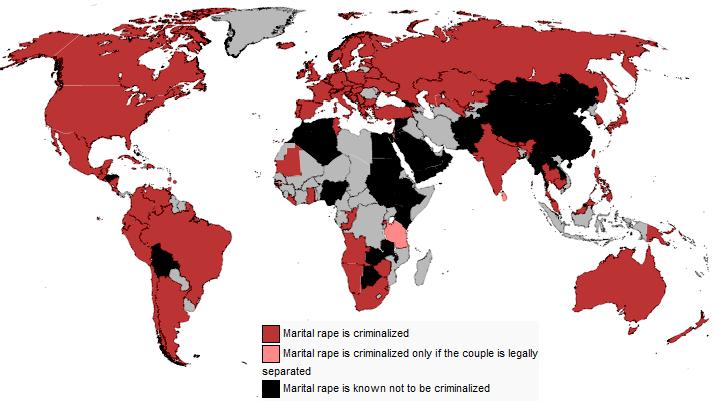
A modern issue associated with rape is "marital rape". This is a subject within the broader context of "spousal abuse", a subject which has received increased public attention particularly as a result of the O.J. Simpson murder trial. Spousal rape is presently a crime in all states although a majority of states provide some exemptions to the husband. These exemption statutes typically address the degree of physical force used.  Researchers estimate that between 10% and 14% of married women experience rape in marriage. Yet prosecutions are not very common. A majority of countries do not have criminal statutes addressing "marital rape". Researchers estimate that between 10% and 14% of married women experience rape in marriage. Yet prosecutions are not very common. A majority of countries do not have criminal statutes addressing "marital rape". 
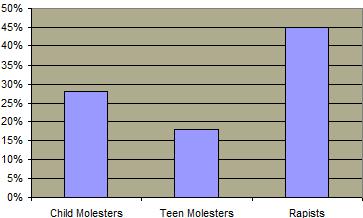
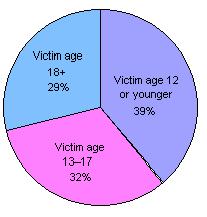
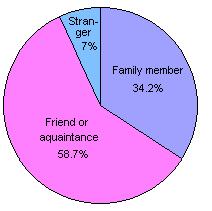
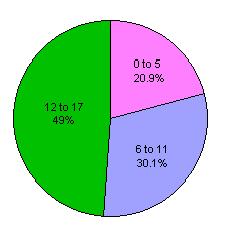
Child sexual abuse, while also on the decline, has received considerable attention during the recent decade. In fact most of those incarcerated in state prisons for sexual offenses have victimized children.  The overwhelming percentage of these sexual assaults are perpetrated by family or friends. The overwhelming percentage of these sexual assaults are perpetrated by family or friends.  Most of the victims are girls and about half are under the age of 12. Most of the victims are girls and about half are under the age of 12.  The perpetrators of these crimes are quite likely to have been abused themselves as children. The perpetrators of these crimes are quite likely to have been abused themselves as children.  There are various studies regarding the degree to which sex offenders repeat their behavior and the results of these studies vary. In general, child abusers are more likely to repeat their behaviors than rapists or those convicted of incest. As with rapists, child sex abusers also often have a history of non-sexual criminal offenses. There are various studies regarding the degree to which sex offenders repeat their behavior and the results of these studies vary. In general, child abusers are more likely to repeat their behaviors than rapists or those convicted of incest. As with rapists, child sex abusers also often have a history of non-sexual criminal offenses.
Are treatment programs for sex offenders successful?
The majority of sex offender treatment programs in the United States and Canada now use a combination of cognitive-behavioral treatment and relapse prevention. Different types of offenders typically respond to different treatment methods with varying rates of success. The only major treatment outcome study to date has found a small, yet significant treatment effect-an 8% reduction in the recidivism rate. Research also demonstrates that sex offenders who fail to complete treatment programs are at increased risk for both sexual and general recidivism. Some studies have shown that the rate of recidivism for sex offenders can be predicted by measuring a prisoner's interest sexual interest in nonsexual violence and degree of psychopathy.
The recidivism problem has prompted twenty states to pass legislation requiring the civil commitment of certain sex offenders who have finished their prison terms.  Nine states now require chemical castration for certain categories of sex offenders. Nine states now require chemical castration for certain categories of sex offenders. 
What registration requirements exist for sex offenders?
Highly publicized sex crimes committed by repeat offenders prompted state legislatures to ratify laws that increase social controls on these offenders. With the passage of the Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act in 2007 there is a federal coordinated registry of sex offenders.
It is unclear whether the system has achieved its goals of protecting families from sexual predators. A family is unlikely to learn of a neighbor with a sexual offense history unless there has been a reason to become suspicious or there has been an aggressive notification campaign in the neighborhood. In the instances where the identity of the predator has been publicized, the individuals have often been harassed. Because of these problems, the registry systems have been opposed by civil liberty organizations.
Criminal Sexual Behavior Links
Google Directory - Rape
Yahoo Directory - Rape
Google Directory - Sexual Assault and Abuse
Google Directory - Child Abuse
Wikipedia - Rape
Wikipedia - Rape Statistics
Wikipedia - Rape in the United States
Wikipedia - Marital Rape
Wikipedia - Child Abuse
Wikipedia - Sex Offender Registration
Rape Abuse and Incest National Network
Office of Criminal Justice Statistics - Rape and Sexual Assault
National Criminal Justice Reference System
|
Charts
(click to enlarge)
Rapes Per 1000 Persons 1973-2009
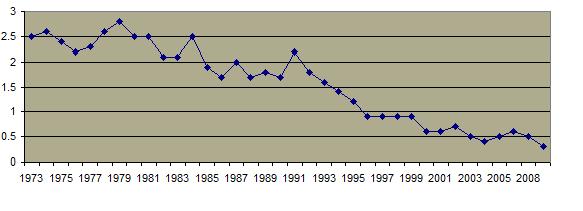
Total Violent Crime Rate Per 1000 Persons, 1973-2009
Child Sexual Abuse 1990-2000
Incidence of Rape in Selected Countries
Lifetime Rape Victimization of Women
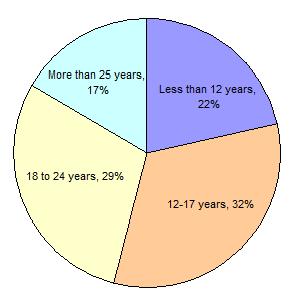
Percentage of Sexual Crimes Reported to Police
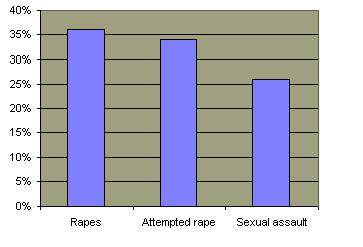
Reporting Rapes by Relationship of Predator
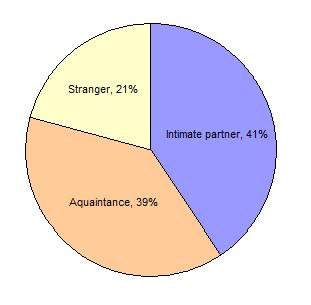
Relationship of Rape Victims to Offender, 2009
Probability of Successful Prosecution of Rape
Criminal Records of Rapists in State Prison
Percentage of Substance Abuse Among Sex Offenders
States Treating Marital Rape Equal to Other Rape Crimes
Global Criminality of Marital Rape
Distribution of Inmates in State Prisons by Age of Victim
Relationship of Child Abuse Perpetrator to Victim
Age of Female Victims of Child Sexual Assaults
Inmates Reporting Physical or Sexual Abuse as Children
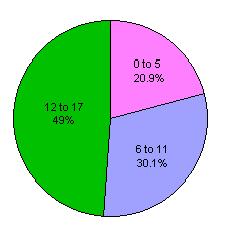
States with Legislation on Civil Commitment of Sex Offenders
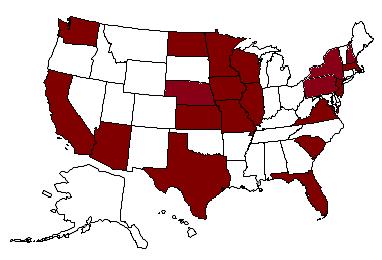
States with Chemical Castration Laws for Specified Sex Offenders
|
|
SEXUAL HARASSMENT
How has "sexual harassment" become an important issue?
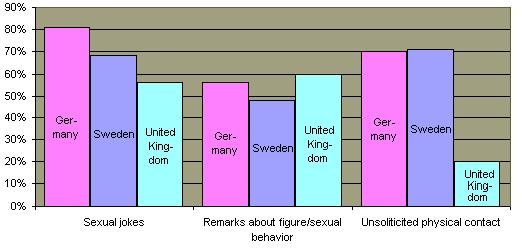
The concern about sexual harassment has coincided with the massive entry of women into all are2011 the American work force during the past three decades. In 1979 Congress held hearings to investigate sexual harassment in the federal government, and the White House Office of Personnel issued a directive prohibiting sexual harassment. In 1980, the first major workplace survey of sexual harassment involved federal workers and these surveys have been repeated twice. These surveys indicate that there has been little change in the frequency of harassment behaviors even with increased public awareness and employer liability.  According to many surveys, workplace sexual harassment is quite common, particularly in the military. According to many surveys, workplace sexual harassment is quite common, particularly in the military.  Research indicates that similar or greater rates of sexual harassment occur in European countries. Research indicates that similar or greater rates of sexual harassment occur in European countries. 
In 1991, Anita Hill submitted a confidential affidavit to the Senate Judiciary Committee, charging that Supreme Court nominee Clarence Thomas had sexually harassed her from 1981 to 1983. Senate hearings on this charge were held in October. Ms. Hill's charges and the hearings have had long-lasting effects on the nation's understanding of sexual harassment
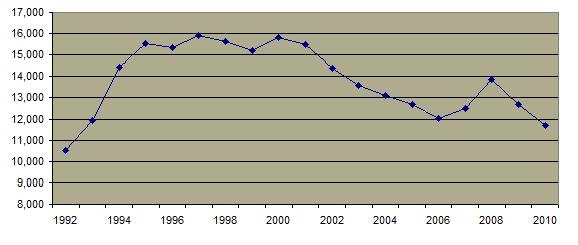
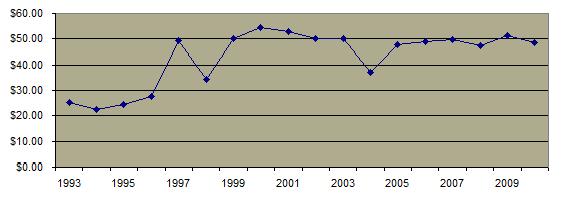
Since the inception of EEOC processing of sexual harassment complaints, the number of formal complaints  and amount of monetary awards and amount of monetary awards  has steadily increased. An increasing percentage of complaints involve male victims. has steadily increased. An increasing percentage of complaints involve male victims.  Only a very small percentage of actual instances of harassment are processed as formal complaints and the most common reaction by women is to ignore the behavior. Only a very small percentage of actual instances of harassment are processed as formal complaints and the most common reaction by women is to ignore the behavior. 
The harassment problem is not limited to the workplace. Surveys have indicated that boys and girls are regularly subjected to various forms of sexual harassment at school.  This harassment substantially interferes with the educational process, most particularly for girls. This harassment substantially interferes with the educational process, most particularly for girls.  Inevitably, increased awareness and employer liability for sexual harassment will eventually reduce these behaviors the workplace and educational environment. But these behaviors are inevitably exacerbated by the overall cultural emphasis on sexuality which affect the behaviors of many individuals of both sexes in our society.
Sexual Harassment Links
Yahoo Directory - Sexual Harassment
Wikipedia - Sexual Harassment
Wikipedia Hostile Environment Sexual Harassment
|
Charts
(click to enlarge)
Trends in Sexual Harrassment Among Federal Workers
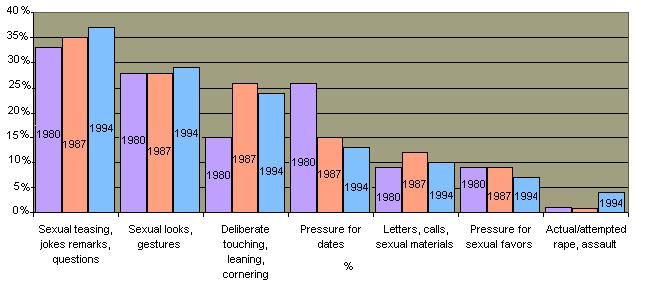
Sexual Harrassment Complaints of Surveyed Military Women
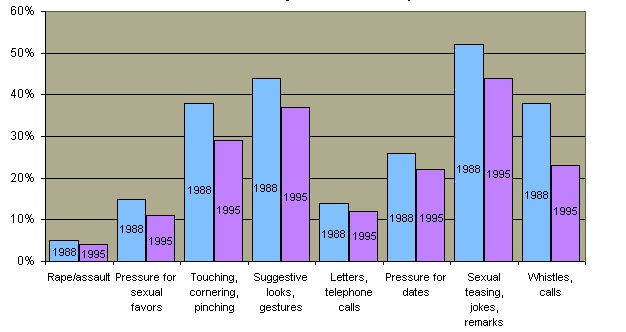
Workplace Harrassment in European Countries
Sexual Harassment Charges Filed with EEOC
Awards Processed by the EEOC 1992-2010
Percentage of Sexual Harassment Charges Involving Men, 1992-2010
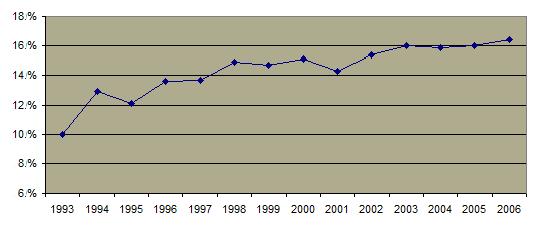
Common Reaction to Sexual Harassment by Federal Employees
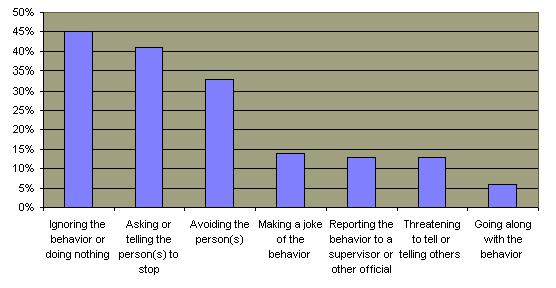
Sexual Harassment in High Schools
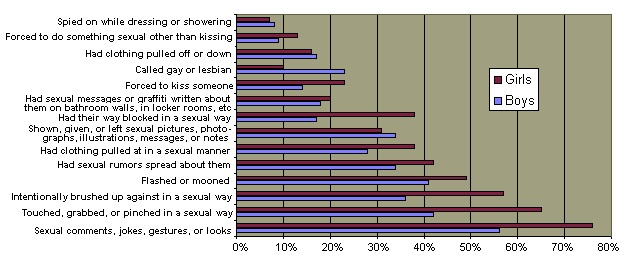
Educational Impact of High School Sexual Harassment
|
|

